Code is copied!

CSS
What is CSS ?
- CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
- It describes how HTML elements are to be displayed on screen,
In other words it is used to beautify our webpages.
Why we use CSS ? Why not just use HTML ?
HTML was created only to describe the content of a web page, like:
<h1> This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
But how this content should look like, this is something which we
can’t achieve with HTML.
That’s why CSS was introduced to present our HTML content beautifully.
HTML Layout
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is heading1</h1>
<p>This is an paragraph </p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is heading1</h1>
<p>This is an paragraph </p>
</body>
</html>
CSS Syntax :
A CSS rule consists of a selector and a declaration block.
Syntax:
selector
{
Property 1:value;
Property 2:value;
}
- The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
- Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon
CSS Selector
- CSS selectors are used to "find" (or select) the HTML elements you want to style.
- It contains various types of selectors but the main are : element, class & id .
element selector
The element selector selects HTML elements based on the element name.
Example: Here, all <p> elements on the page will be center-aligned, with a red text color
p {
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
p {
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
id selector
- The id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML element
to select a specific element.
- The id of an element is unique within a page, so the id selector is used to
select one unique element.
- To select an element with a specific id, write a hash (#) character,
followed by the id of the element.
Example: The CSS rule below will be applied to the HTML element with id="para1"
#para1
{
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
Note: An id name cannot start with a number.
#para1
{
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
class selector
- The class selector selects HTML elements with a specific class attribute.
- To select elements with a specific class, write (.) character, followed by the class name.
Example: In this example all HTML elements with class="center" will be red and center-aligned:
.center {
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
You can also specify that only specific HTML elements should be
affected by a class.
In this example only <p> elements with class="center" will be
red and center-aligned
p.center{
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
.center {
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
p.center{
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
Universal selector
The universal selector (*) selects all HTML elements on the page.
Example: The CSS rule below will affect every HTML element on the page
* {
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
* {
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
Grouping selectors
Grouping selectors will selects all the HTML elements
with the same style definitions.
Example: In this example we have grouped the selectors with the same styles
h1.p{
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
h1.p{
text-align:center;
color:red;
}
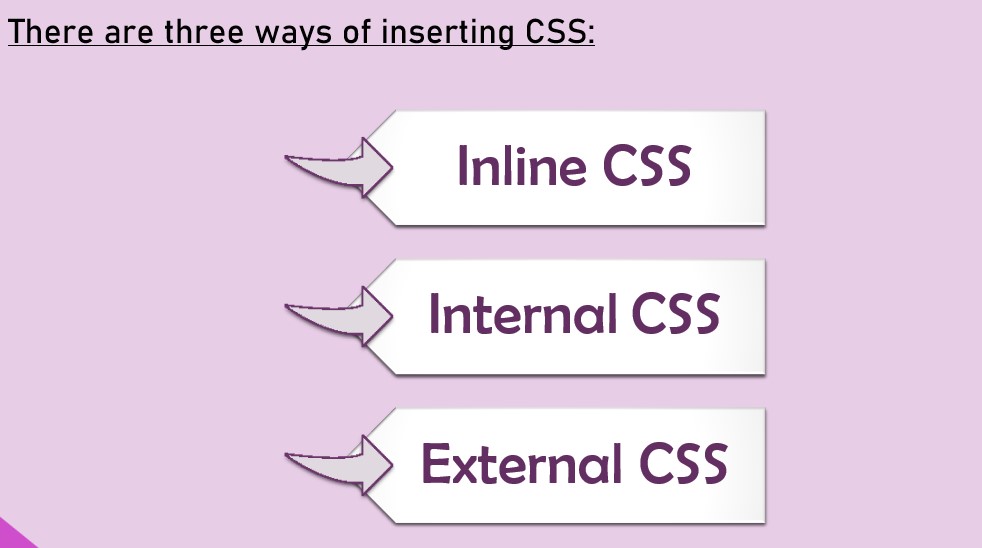
How to add CSS in our HTML
Inline CSS
An inline style may be used to apply a unique style for a single element. To use inline styles, add the style attribute to the relevant element. The style attribute can contain any CSS property.
Example: Inline styles are defined within the "style" attribute of the relevant element:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="color:blue;text-align:center;">This is heading1</h1>
<p style="color:red;" >This is an paragraph </p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="color:blue;text-align:center;">This is heading1</h1>
<p style="color:red;" >This is an paragraph </p>
</body>
</html>
Internal CSS
An internal style sheet may be used if one single HTML page has a unique style.
The internal style is defined inside the <style> element, inside the head section
Example: Internal styles are defined within the <style> element, inside the <head> section of an HTML page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First website</title>
<style>
h1,p {
color: blue;
padding-left:40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is heading1</h1>
<p>This is an paragraph </p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First website</title>
<style>
h1,p {
color: blue;
padding-left:40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is heading1</h1>
<p>This is an paragraph </p>
</body>
</html>
External CSS
With an external style sheet, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file. Each HTML page must include a reference to the external style sheet file inside the <link> element, inside the head section
Example: External styles are defined within the <link> element, inside the <head> section of an HTML page. The file must be saved with (.css) extension
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First website</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mystyle.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is heading1</h1>
<p>This is an paragraph </p>
</body>
</html>
mystyle.css file
body{
background-color:aliceblue;
}
h1{
color:navy;
text-align:center;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First website</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mystyle.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is heading1</h1>
<p>This is an paragraph </p>
</body>
</html>
body{
background-color:aliceblue;
}
h1{
color:navy;
text-align:center;
}
CSS Properties
CSS Backgrounds:
>> background-color : Sets the background color of an element
Example:
background-color: lightblue;
>> background-image : Sets the background image of an element
Example:
background-image: url(“flower.jpg");
>> background-size : Sets the width and height of the background image
Example:
background-size: auto;
background-size: contain;
background-size : cover;
CSS RGB Colors
[R: RED(0-255) ; G: GREEN(0-255) ; B: BLUE(0-255)[0: white | 255: complete red, green, blue]
Example:
background-color: rgb(255, 99, 71);
You can also make color transparent using one more option in rgb is ‘a’ i.e. rgba where a stands for transparency in color whose value lies between 0 and 1 (where 0 is fully transparent and 1 is not transparent)
Example :
background-color: rgba(255, 99, 71,0.5);
CSS Color:
>> color : Specifies the color of the text
Example:
color:red;
CSS Text:
>> text-align : Specifies the horizontal alignment of text
Example:
text-align: left;
>> text-transform : Specify uppercase and lowercase letters in a text
Example:
text-transform:uppercase;
text-transform:lowercase;
text-transform:capitalize;
>> letter-spacing : Specify spaces between letters in a text
Example:
letter-spacing:3px;
>> word-spacing : Specify spaces between word in a sentence
Example:
word-spacing:3px;
>> line-height : Specify spaces between lines in a paragraph
Example:
line-height:3px;
CSS Font:
>> font-size : Specifies the size of font
Example:
font-size:2px;
>> font-style : property is mostly used to specify italic text.
Example:
font-style: italic;
font-style:oblique;
>> font-weight: Specifies the weight of font
Example:
font-weight:500;
>> font-family: Specifies the font family of the text
Example:
font-family:'Roboto','sans-serif';
CSS Borders:
>> border-style : Specifies what kind of border to be displayed
Example:
border-style:solid;
border-style:dashed;
border-style:dotted;
border-style:double;
border-style:none;
>> border-color : Specifies what color of border to be displayed.
Example:
border-color:red;
>> border-radius: Specifies rounded corners for the border element.
Example:
border-radius:20px;
border-radius:50%;
>> border-width: Specifies the width of border
Example:
border-width:20px;
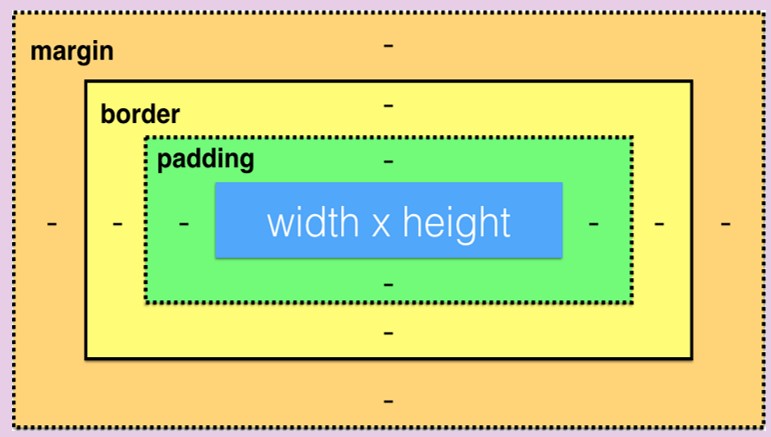
CSS Margins:
Margins are used to create space around elements, outside of any defined borders.
- If margin property have one value
Example : margin:25 px;
All four margins are 25px.
- If margin property have only two values
Example : margin:25px 50px;
top and bottom margins are 25px
right and left margins are 50px
- If margin have only three values
Example : margin: 10px 20px 30px;
top margin is 10px
right and left margins are 20px
bottom margin is 75px
- If margin have all four values
Example : margin: 20px 10px 15px 25px;
top margin is 20px; right margin is 10px
bottom margin is 15px; left margin is 25px
CSS Paddings:
Padding are used to create space around elements, inside of any defined borders.
- If padding property have one value
Example : padding:25 px;
All four paddings are 25px.
- If padding property have only two values
Example : padding:25px 50px;
top and bottom paddings are 25px
right and left paddings are 50px
- If padding have only three values
Example : padding: 10px 20px 30px;
top padding is 10px
right and left paddings are 20px
bottom padding is 75px
- If padding have all four values
Example : padding: 20px 10px 15px 25px;
top padding is 20px; right padding is 10px
bottom padding is 15px; left padding is 25px
background-color: lightblue;
background-image: url(“flower.jpg");
background-size: auto;
background-size: contain;
background-size : cover;
background-color: rgb(255, 99, 71);
background-color: rgba(255, 99, 71,0.5);
color:red;
text-align: left;
text-transform:uppercase;
text-transform:lowercase;
text-transform:capitalize;
letter-spacing:3px;
word-spacing:3px;
line-height:3px;
font-size:2px;
font-style: italic;
font-style:oblique;
font-weight:500;
font-family:'Roboto','sans-serif';
border-style:solid;
border-style:dashed;
border-style:dotted;
border-style:double;
border-style:none;
border-color:red;
border-radius:20px;
border-radius:50%;
border-width:20px;