Class 9th Java aims to empower students by enabling them to build
their own applications introducing some effective tools to
enable them to enhance their knowledge, broaden
horizons, foster creativity, improve the quality of
work and increase efficiency.
It also develops logical and analytical thinking so that
they can easily solve interactive programs.
Students learn fundamental concepts of
computing using object oriented approach in one
computer language with a clear idea of ethical
issues involved in the field of computing
Class 9th java topics includes revision of class 9th, constructors, user-defined methods, objects and
classes,
library classes , etc.
Definition
Full form of OOPS is Object Oriented Programming Structure/System.It is a programming system which is
based on concept of objects.Each of these objects are used to perform specific actions
It is also said to be a programming paradigm methodology,here programming paradigm means a method to
solve problems using programming language.So OOP is a method which use object to write programs and solve
problems.
There are 6 main concept or we can say pillars of OOPS,these are:-
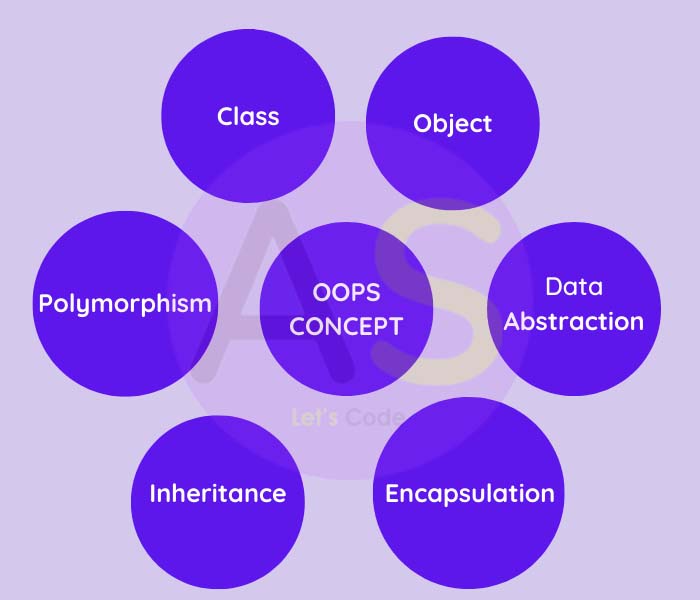
Let us understand each concept one by one in detail.
Object
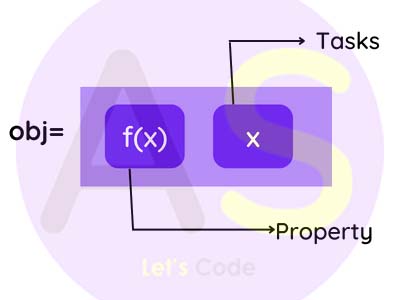
It is defined as a real life entity,whatever we see in real life is termed as an object.These entities have
some properties and task to perform.It is a basic unit of object-Oriented Programming language.
An object is also said to an instance of class,that is ,it will follow all the prototype defined by the
class.There can be mutliple instance of a class in a program.
An object consists of:-
-
unique Identity:Each object has unique Identity,that enable object to interact with other
objects
-
Behavior: It tells what object does.It can be used a response for one object to other objects
-
State/Properties/Attributes: It tells how the object will look like.
Let us understand this real-life entity by an example:-

In implementing this real-world object in software form,all these Attributes are represented through
data items known as member variables and Behavior are represented through
methods known
as member methods.

Classes
A class is one of the basic concepts of OOPS,it is the collection of objects.Without a class object is
nothing.
A class is declared by use of the class keyword. The class body is enclosed between curly braces {
and }.
The data or variables, defined within a class are called instance variables.The code is contained
within methods of a class.
It has some properties and tasks,and each object must follow these prototypes defined in the class.
Let us understand this by example
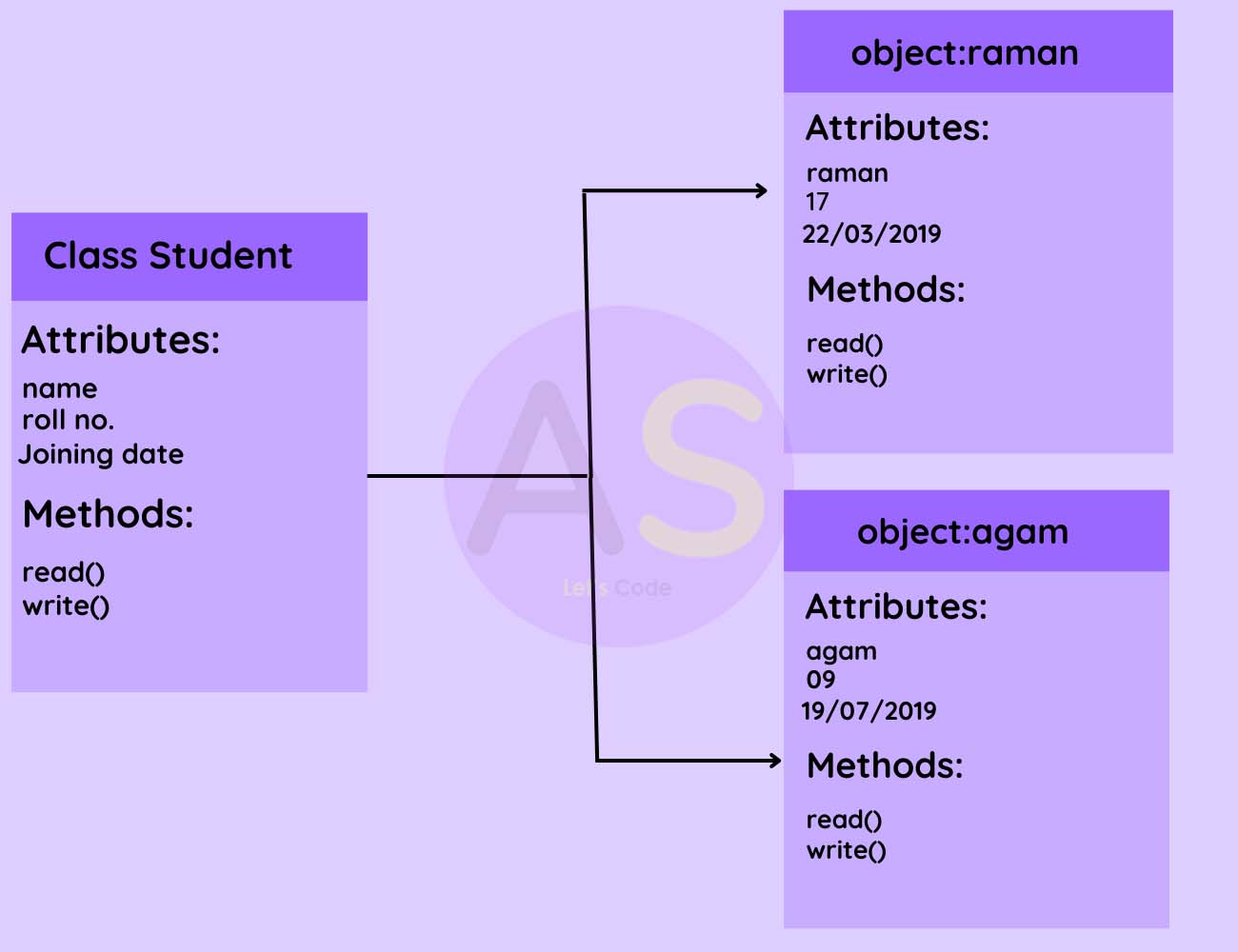
From the above example,we can observe that each objects named as agam and raman,follow attributes of a class
such as name,roll
number,joining data and methods of a class such as read(),write().
Syntax :
From the above syntax we can say that "Class is a collection of data and
methods."
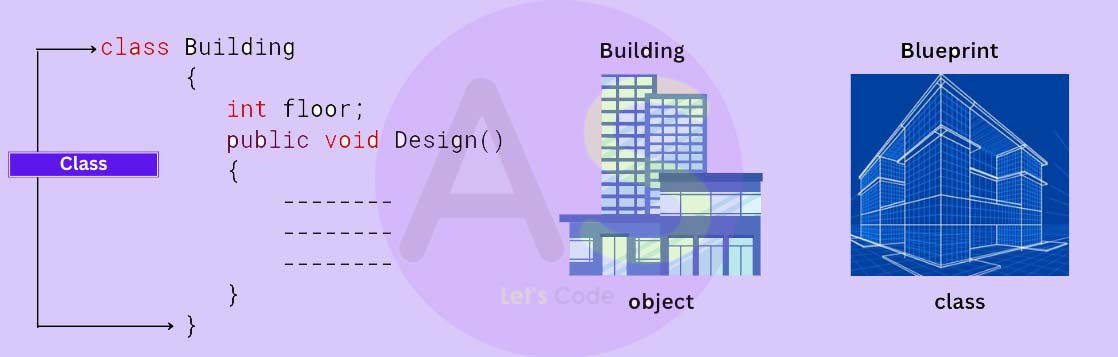
Example : If we have to build a building then we require a structure por blueprint to build it. So this
building is an object and that blueprint is a class.
So to define object what object knows and what object does we use class.
Polymorphism
If a function behaves differntly for different objects then this is known as polymorphism.It is
one of the OOPs concept in java in which methods and variables can have different forms.
Function overloading is an example of polymorphism.
Let us discuss about method overloading defination and example given below
Method Overloading
The functions having the same name but have different numbers of parameters passed to it, which can
have different data types like int, double, float and used to return different values are known as
overloaded method. This process is known as function overloading
Consider the above two declarations :
The above mentioned two methods have the same name but different parameter declaration if you call
min() with int parameter then min() method that expects int parameter will be invoked and if you
call min() with double parameters the min() method that expects double parameters will be invoked.
This referred to as method overloading and method min() is said to be overloaded
Encapsulation
Encapsulation in Java is wrapping the data (variables) and code acting on data (method)
together
as a single unit.
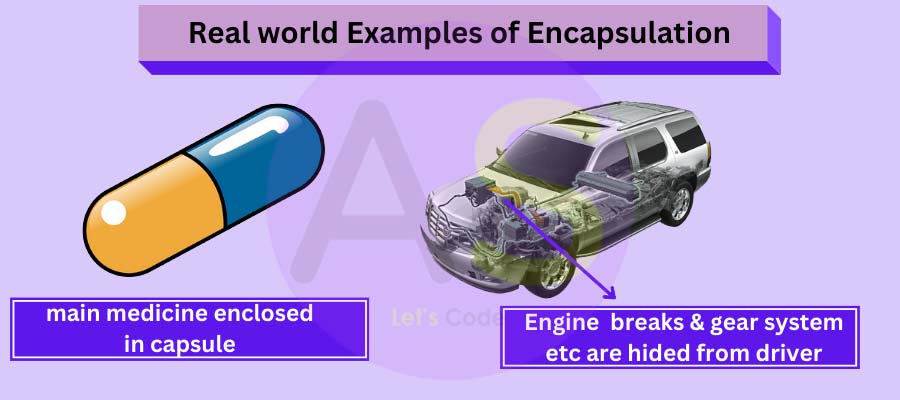
Real world example of encapsulation :
Steps to achieve Encapsulation
- Declare the variable of a class as private
- Provide public setter and getter methods to modify and view the variable values.
In encapsulation the variables of a class (data) will be hidden from
other
classes and can be accessed only through the methods of their current class. This method is
called data hiding
Abstraction
It is one of the OOPs concept in which we show only essential parts and hide the implementiion
details.The non-essential parts are not displayed to the users.
Let us understand this by an example:
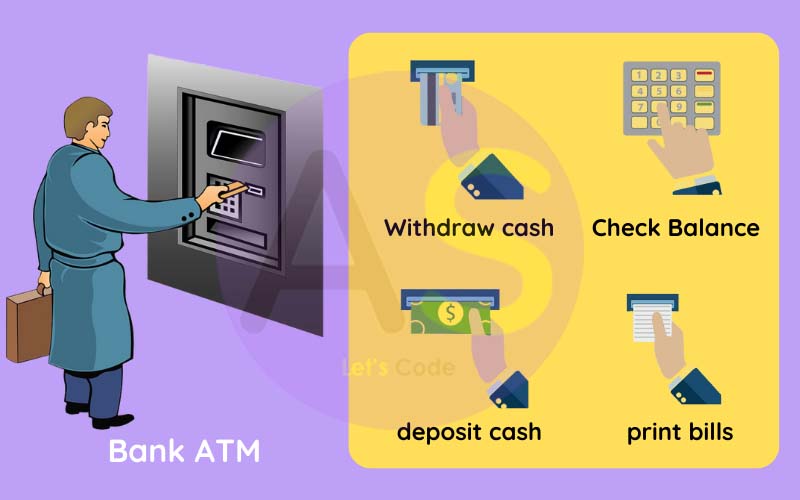
The above example is of ATM machine.In an ATM machine,we peform function like withdraw
cash,deposit cash,check balance,print bills,and so on.Since it performs a lot of actions,it
doesn’t show us the process. It hiddes its process by showing only the main things like getting
inputs and giving the output.
Inheritance
It is one of the OOPs concept in which we acquire the properties of one class to another class.
It has one parent class known as base class and can have more than one child class
which is known as derived class,and Inheritance allows child classes to inherit properties from
parent class.
Let us understand by an example:-
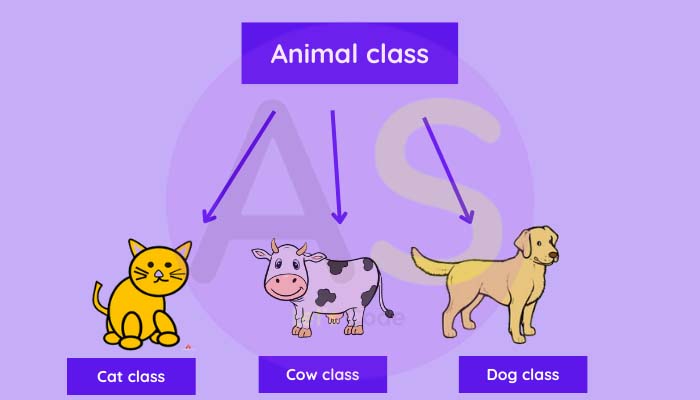
In the above example here animal class is a parent class,and these
dog class,cow
class and cat class are child classes which are derived from animal class,and these child
classes
inherit some common properties
and
Behavior from
animal class.