Code is copied!
CLASS 12 ISC JAVA SPECIMEN PAPER 2022 Term - II
Maximum Marks: 35
Time allowed: One and a half hour
Candidates are allowed an additional 10 minutes for only reading the paper.
They must NOT start writing during this time.
Answer all questions in Section A, Section B and Section C.
While answering questions in Sections A and B, working and reasoning may be
indicated briefly.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets. [ ]
All working, including rough work, should be done on the same sheet as the
rest of the answer.
Section - A (7 marks)
Question 1
(i) The keyword used by a class to acquire the properties of an interface is:
- import
- implements
- extends
- include
Solution
(II)
implements
(ii) The ability of an object to take many forms is known as:
- inheritance
- data abstraction
- overriding
- polymorphism
Solution
(IV)
polymorphism
(iii)
int Toy(int n)
{ return (n
<=0)? 1: n%10 + Toy(n/10); }
With reference to the program code given above, what will the function
Toy() return when the value of n=56 ?
- 65
- 12
- 651
- 11
Solution
(II)
12
(iv) Write the statement in Java to extract the word “MISS” from the word “SUBMISSION”.
Solution:
String s="SUBMISSION"
s=s.substring(3,7); //MISS
(v) State the principle by which the stack data structure works.
Solution:
Stacks in Data Structures is a linear type of data structure that follows the LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) principle and allows insertion and deletion operations from one end of the stack data structure, that is top. Implementation of the stack can be done by contiguous memory which is an array, and non-contiguous memory which is a linked list. Stack plays a vital role in many applications.
(vi)
What is the output of the statement given below?
System.out.print("FAN" + ("AUTOMATIC".charAt(5) ) );
Solution:
The Output of given statement is:
FANA
//FAN+A(CharAt is used to extract a single char from a whole word)
(vii) Give one reason, why iteration is better than recursion.
Solution:
Iteration is better than recursion when time complexity is the point of focus, and number of recursive calls would be large, it is better to use iteration. However, if time complexity is not an issue and shortness of code is, recursion would be the way to go
Section - B (8 marks)
Question 2
Differentiate between direct recursion and indirect recursion.
Solution:
| Direct Recursion | Indirect Recursion |
|---|---|
| In the direct recursion, only one function is called by itself. | In indirect recursion more than one function are by the other function and number of times. |
| direct recursion makes overhead. | The indirect recursion does not make any overhead as direct recursion |
| The direct recursion called by the same function | While the indirect function called by the other function |
Convert the following infix notation to postfix notation:
A * (B + C / D ) – E / F
Solution
ABCD/+*EF/
Answer the following questions on the diagram of a Binary Tree
given below:
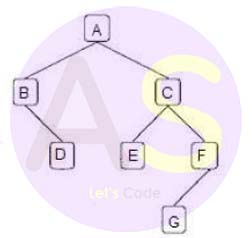
-
State the degree of the nodes C and G. Also, state the level of
these nodes when the root is at level 0.
Solution:
Degree of C is 2
Degree of G is 0
Level of C will be 1,when root is at level 0
Level of G will be 3,when root is at level 0
-
Write the pre order and post order traversal of the above tree
structure.
Solution:
Preorder:
A->B->D->C->E->F->G
Postorder:
D->B->E->G->F->C->A
SECTION C (20 marks)
Question 5 (i)
Design a class Check which checks whether a word is a palindrome or not.
(Palindrome words are those which spell the same from either ends).
Example: MADAM, LEVEL etc.
The details of the members of the class are given below:
Class name : Check
Data members/instance variables:
wrd : stores a word
len : to store the length of the word
Methods/Member functions:
Check( ) : default constructor
void acceptword( ) : to accept the word
boolean palindrome ( ) : checks and returns ‘true’ if the word is
a palindrome otherwise returns ‘false’
void display( ) : displays the word along with an
appropriate message
Specify the class Check giving details of the constructor, void acceptword( ),
boolean palindrome( ) and void display( ). Define the main( ) function to create
an object and call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Solution:
import java.util.*;
class check{
String wrd;int len;
check(){
wrd="";
len=0;
}
void acceptword(){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the word");
wrd=sc.nextLine();
len=wrd.length();
}
boolean palindrome(){
String s="";
for(int i=0;i< len; i++ ) {
s=s+wrd.charAt(i);
}
if(wrd.equals(s)) {
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
void display(){
boolean chk=palindrome();
if(chk== true){
System.out.println(wrd+" is a palindrome number " );
}
else{
System.out.println(wrd+ " is not a palindrome number" );
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
check ch=new check();
ch.acceptword();
ch.display();
}
}
Question 5 (ii)
Design a class Toggle which toggles a word by converting all upper case
alphabets to lower case and vice versa.
Example: The word “mOTivATe” becomes “MotIVatE”
The details of the members of the class are given below:
Class name : Toggle
Data members/instance variables:
str : stores a word
newstr : stores the toggled word
len : to store the length of the word
Methods/Member functions:
Toggle( ) : default constructor
void readword( ) : to accept the word
void toggle ( ) : converts the upper case alphabets to
lower case and all lower case
alphabets to upper case and stores it in
newstr
void display( ) : displays the original word along with
the toggled word
Specify the class Toggle giving details of the constructor, void readword( ),
void toggle( ) and void display( ). Define the main( ) function to create an
object and call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Solution:
import java.util.*;
class Toggle{
String str,newstr;
int len;
Toggle(){
str="";
newstr="";
len=0;
}
void readword(){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the word");
str=sc.nextLine();
len=str.length();
}
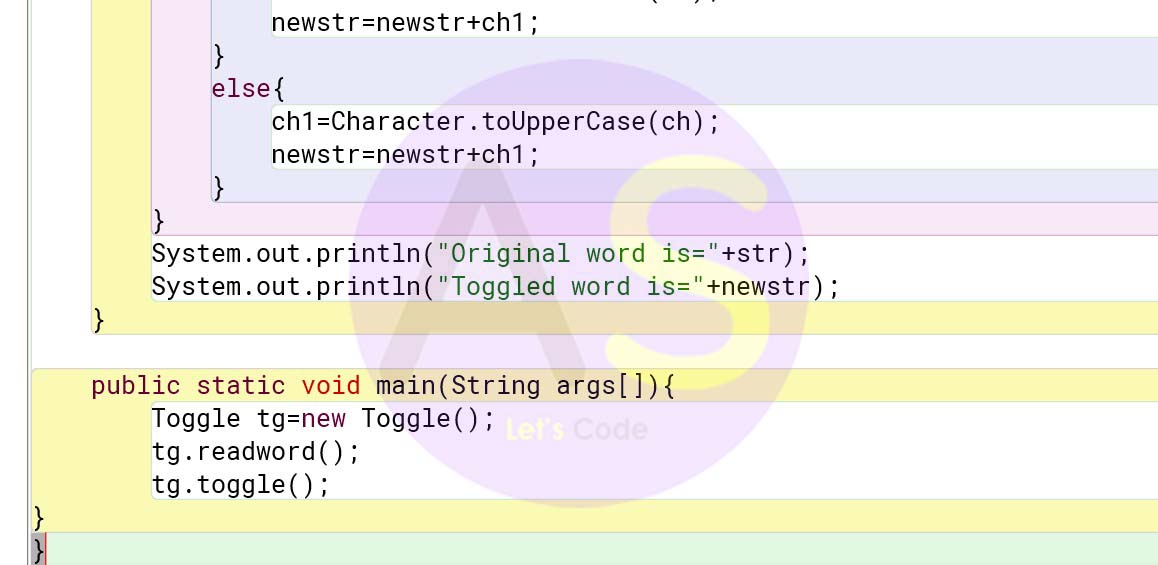
void toggle(){
char ch,ch1;
for(int i=0;i< len;i++){
ch=str.charAt(i);
if(Character.isUpperCase(ch)){
ch1=Character.toLowerCase(ch);
newstr=newstr+ch1;
}
else{
ch1=Character.toUpperCase(ch);
newstr=newstr+ch1;
}
}
System.out.println("Original word is="+str);
System.out.println("Toggled word is="+newstr);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Toggle tg=new Toggle();
tg.readword();
tg.toggle();
}
}
Question 6 (i)
A class Fibo has been defined to generate the Fibonacci series 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5,
8, 13,……. (Fibonacci series are those in which the sum of the previous two
terms is equal to the next term).
Some of the members of the class are given below:
Class name : Fibo
Data member/instance variable:
start : integer to store the start value
end : integer to store the end value
Member functions/methods:
Fibo( ) : default constructor
void read( ) : to accept the numbers
int fibo(int n) : return the nth term of a Fibonacci series
using recursive technique
void display( ) : displays the Fibonacci series from start
to end by invoking the function fibo()
Specify the class Fibo, giving details of the Constructor, void read( ), int
fibo(int), and void display( ). Define the main() function to create an object and
call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Solution:
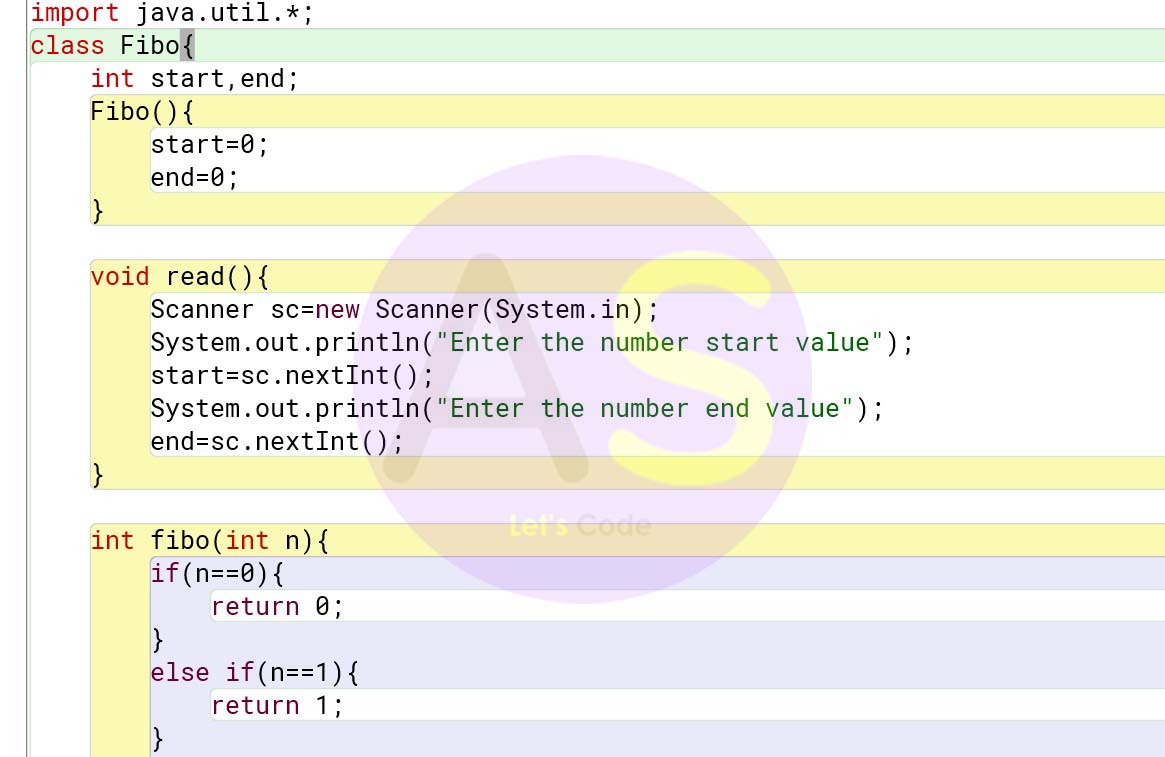

import java.util.*;
class Fibo{
int start,end;
Fibo(){
start=0;
end=0;
}
void read(){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number start value");
start=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the number end value");
end=sc.nextInt();
}
int fibo(int n){
if(n==0){
return 0;
}
else if(n==1){
return 1;
}
else{
return (fibo(n-1)+fibo(n-2));
}
}
void display(){
System.out.print("fibonacci series is=");
for(int i=start;i< end;i++){
System.out.print(fibo(i)+",");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Fibo fb=new Fibo();
fb.read();
fb.display();
}
}
Question 6 (ii)
A class Gcd has been defined to find the Greatest Common Divisor of two
integer numbers. Some of the members of the class are given below:
Class name : Gcd
Data member/instance variable:
num1 : integer to store the first number
num2 : integer to store the second number
Member functions/methods:
Gcd( ) : default constructor
void accept( ) : to accept the numbers
int gcd(int x,int y) : return the GCD of the two number x
and y using recursive technique
void display( ) : displays the result with an appropriate
message
Specify the class Gcd, giving details of the Constructor, void accept( ), int
gcd(int,int), and void display( ). Define the main() function to create an object
and call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Solution:
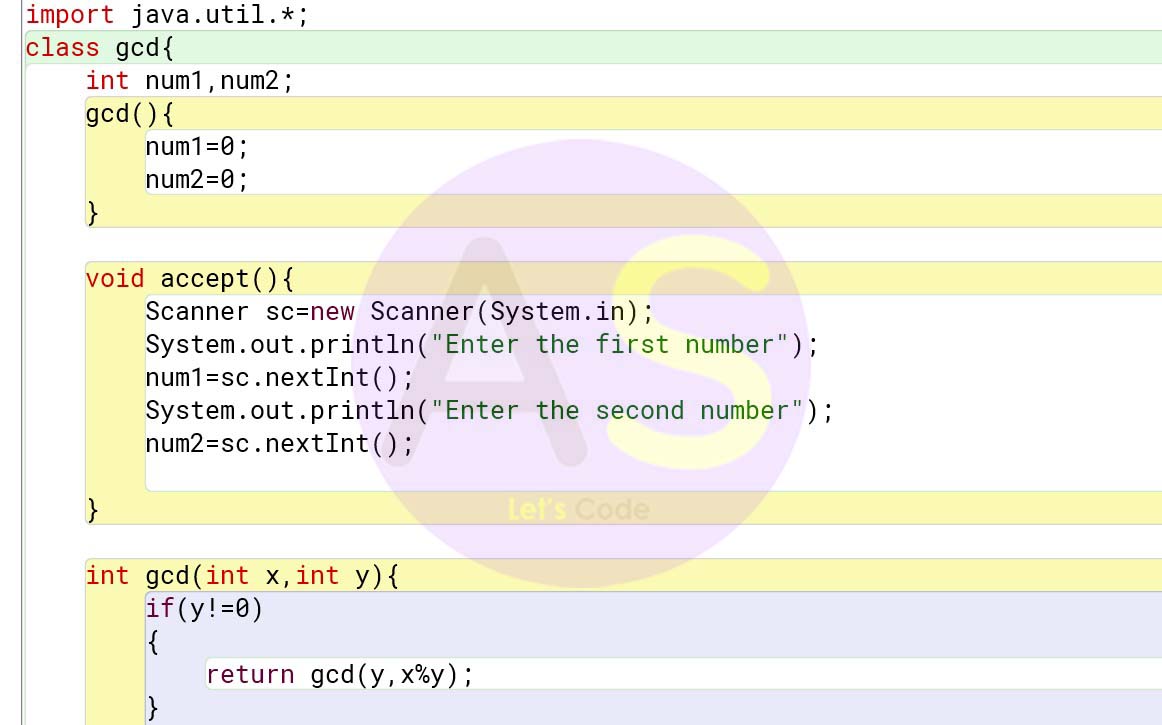
import java.util.*;
class gcd{
int num1,num2;
gcd(){
num1=0;
num2=0;
}
void accept(){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the first number");
num1=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the second number");
num2=sc.nextInt();
}
int gcd(int x,int y){
if(y!=0)
{
return gcd(y,x%y);
}
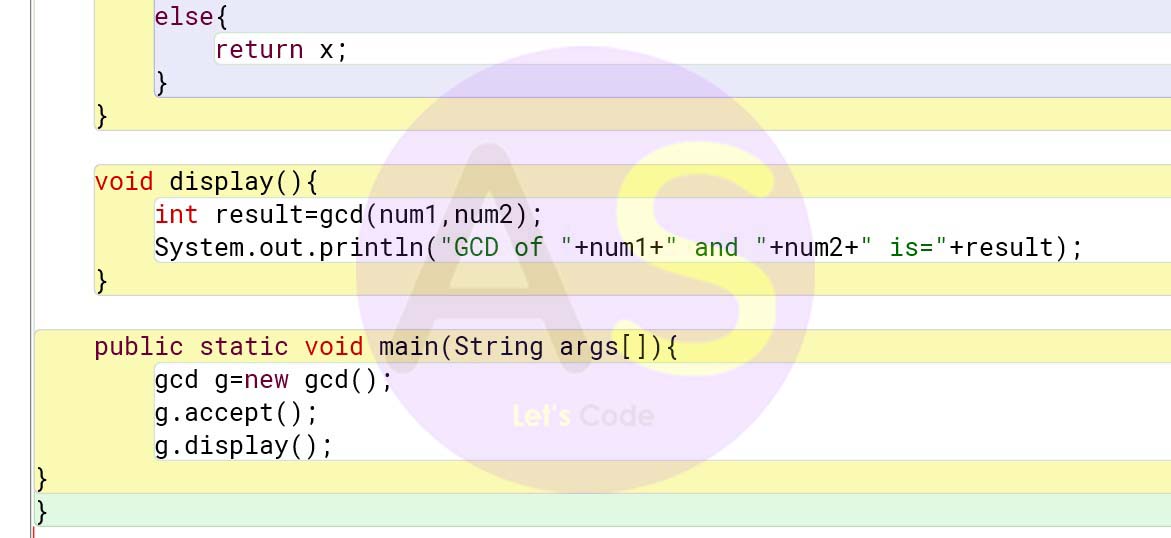
else{
return x;
}
}
void display(){
int result=gcd(num1,num2);
System.out.println("GCD of "+num1+" and "+num2+" is="+result);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
gcd g=new gcd();
g.accept();
g.display();
}
}
Question 7
A super class Godown has been defined to store the details of the stock of a retail
store. Define a subclass Update to store the details of the items purchased with the
new rate and update the stock. Some of the members of both the classes are given
below:
Class name : Godown
Data members/instance variables:
item : to store the name of the item
qty : to store the quantity of an item in stock
rate : to store the unit price of an item
amt : to store the net value of the item in stock
Member functions/methods:
Godown( …) : parameterized constructor to assign value to
the data members
void display( ) : to display the stock details
Class name : Update
Data members/instance variables:
pur_qty : to store the purchase quantity
pur_rate : to store the unit price of the purchased item
Member functions / methods
Update(…) : parameterized constructor to assign values to
the data members of both the classes
void update( ) : to update the stock by adding the previous
quantity by the purchased quantity and
replace the rate of the item if there is a
difference in the purchase rate. Also update
the current stock value as:
(quantity * unit price )
void display( ) : to display the stock details before and after
updating
Assume that the super class Godown has been defined. Using the concept of
inheritance, specify the class Update giving details of the constructor, void update
( ) and void display( ).
The super class, main function and algorithm need NOT be written.
Solution:
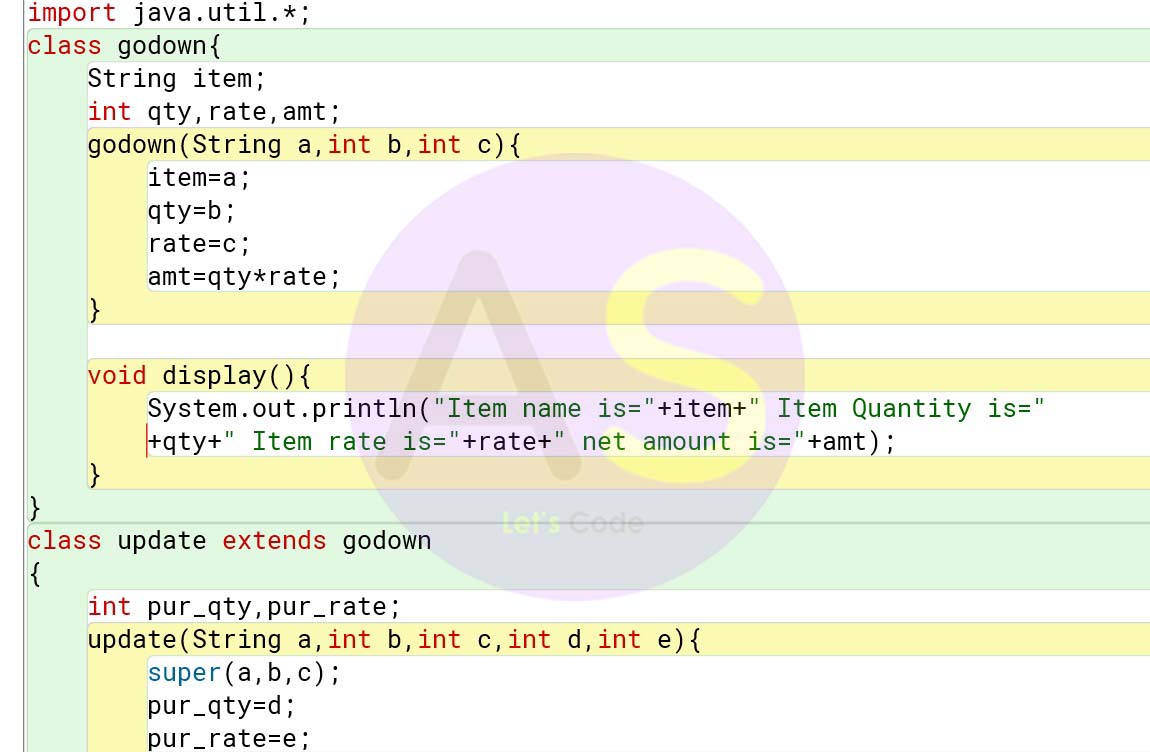

import java.util.*;
class godown{
String item;
int qty,rate,amt;
godown(String a,int b,int c){
item=a;
qty=b;
rate=c;
amt=qty*rate;
}
void display(){
System.out.println("Item name is="+item+" Item Quantity is="+qty+" Item rate is="+rate+" net amount is="+amt);
}
}
class update extends godown
{
int pur_qty,pur_rate;
update(String a,int b,int c,int d,int e){
super(a,b,c);
pur_qty=d;
pur_rate=e;
}
void update(){
qty+=pur_qty;
if(rate!=pur_rate){
rate=pur_rate;
amt=qty*rate;
}}
void display(){
System.out.println("Previous details:");
super.display();
update();
System.out.println("New Details");
super.display();
}
}
Question 8
A Queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on
FIFO (First In First Out).
Define a class Queue with the following details:
Class name : Queue
Data member/instance variable:
dat[ ] : array to hold the integer elements
cap : stores the maximum capacity of the queue
front : to point the index of the front
rear : to point the index of the rear.
Member functions/methods:
Queue(int max) : constructor to initialize the data member
cap = max, front = rear = 0 and create the
integer array
void add_dat(int v) : to add integers from the rear index if
possible else display the message(“Queue
full”)
int pop_dat( ) : to remove and return elements from front,
if any, else returns -999
void display() : to display elements of the queue
Specify the class Queue giving the details of void add_dat(int) and int pop_dat( ).
Assume that the other functions have been defined.
The main( ) function and algorithm need NOT be written.
Solution:
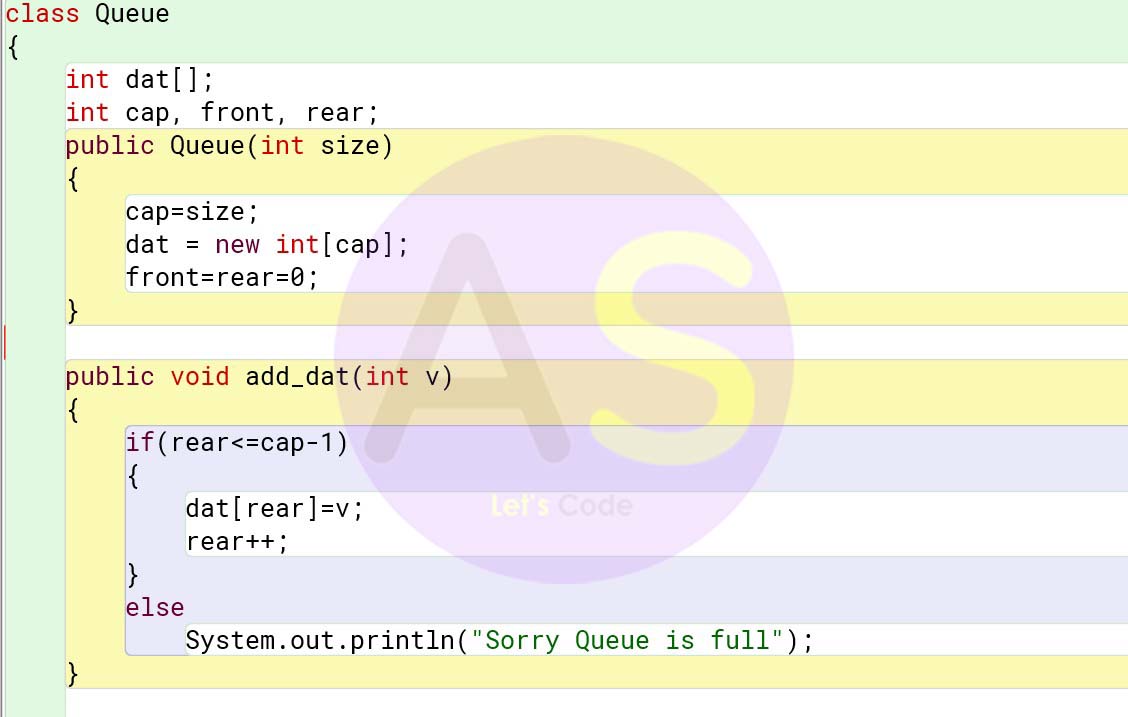
class Queue
{
int dat[];
int cap, front, rear;
public Queue(int size)
{
cap=size;
dat = new int[cap];
front=rear=0;
}
public void add_dat(int v)
{
if(rear<=cap-1)
{
dat[rear]=v;
rear++;
}
else
System.out.println("Sorry Queue is full");
}
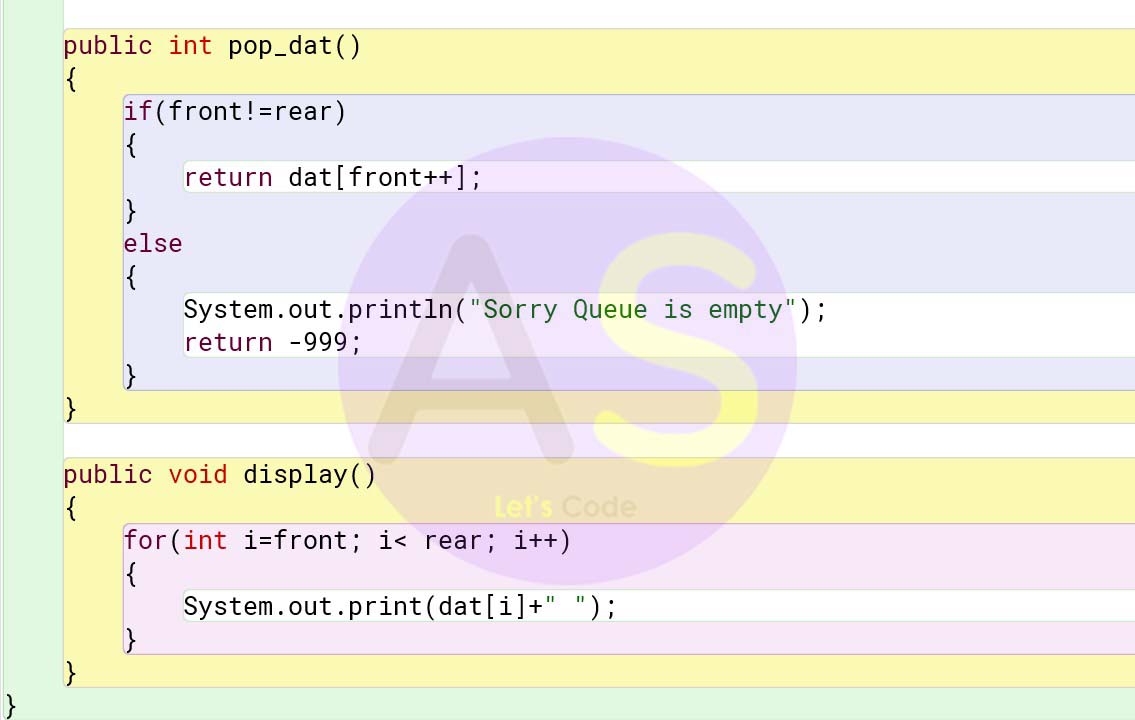
public int pop_dat()
{
if(front!=rear)
{
return dat[front++];
}
else
{
System.out.println("Sorry Queue is empty");
return -999;
}
}
public void display()
{
for(int i=front; i< srear; i++)
{
System.out.print(dat[i]+" ");
}
}
}