Class 12 ISC- Java
Class 12th Java aims to empower students by enabling them to build their own applications introducing some effective tools to enable them to enhance their knowledge, broaden horizons, foster creativity, improve the quality of work and increase efficiency.
It also develops logical and analytical thinking so that they can easily solve interactive programs. Students learn fundamental concepts of computing using object oriented approach in one computer language with a clear idea of ethical issues involved in the field of computing
Class 12th java topics includes revision of class 11th, constructors, user-defined methods, objects and classes, library classes , etc.
Sorting Techniques
Sorting means arranging elements of an array in ascending or descending order.
Bubble Sort
Bubble sort is a sorting algorithm which iterates through a given array of elements and compares each pair of adjacent elements one after the other.
How Bubble Sort works ( For descending order) :
So in this technique we do sorting upto (size - 1), if there are 5 elements, it takes (5-1), i.e 4 iterations to completely sort the array.
In any of the adjacent pairs, if the first element is smaller than the second element, then it swaps the elements and if not, then it moves on to the next pair of elements (i.e. at first we are placing the smallest element at the extreme right and then before that the second smallest element and so on and so forth).
After each iteration, the smallest element among the unsorted elements is placed at the extreme right. At the end the given array is sorted in descending order.
For (I-Iteration) :
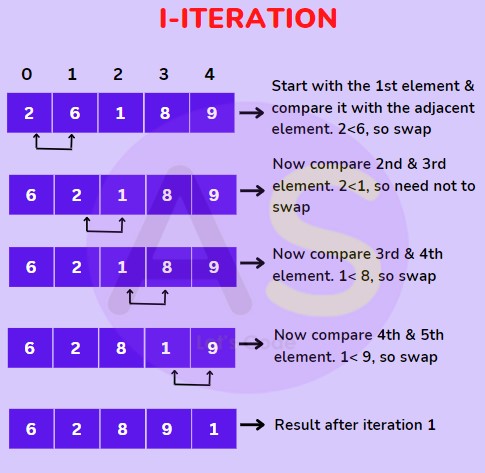
For (II-Iteration) :
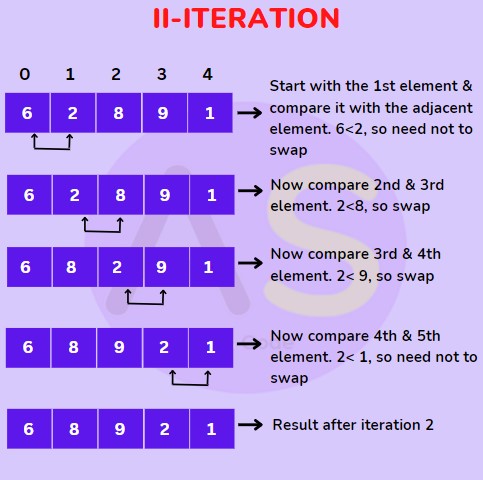
For (III-Iteration) :
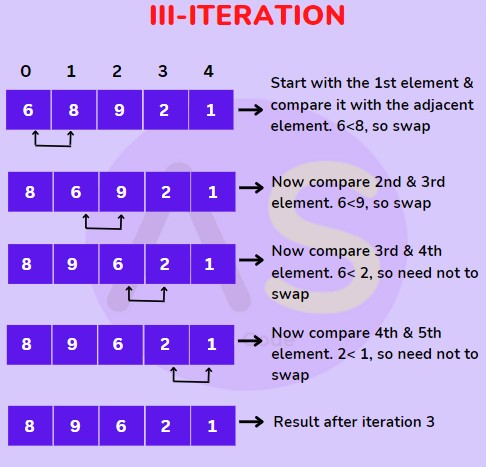
For (IV-Iteration) :
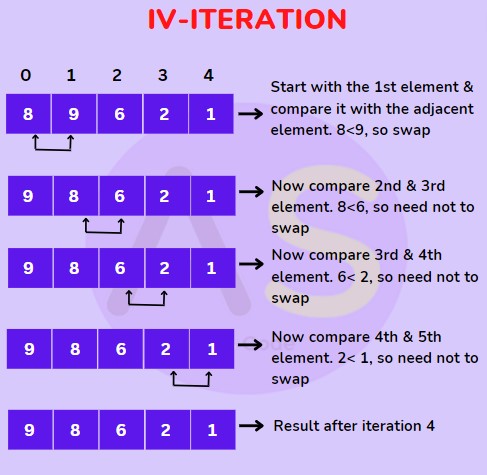
For user-defined values :
Program :
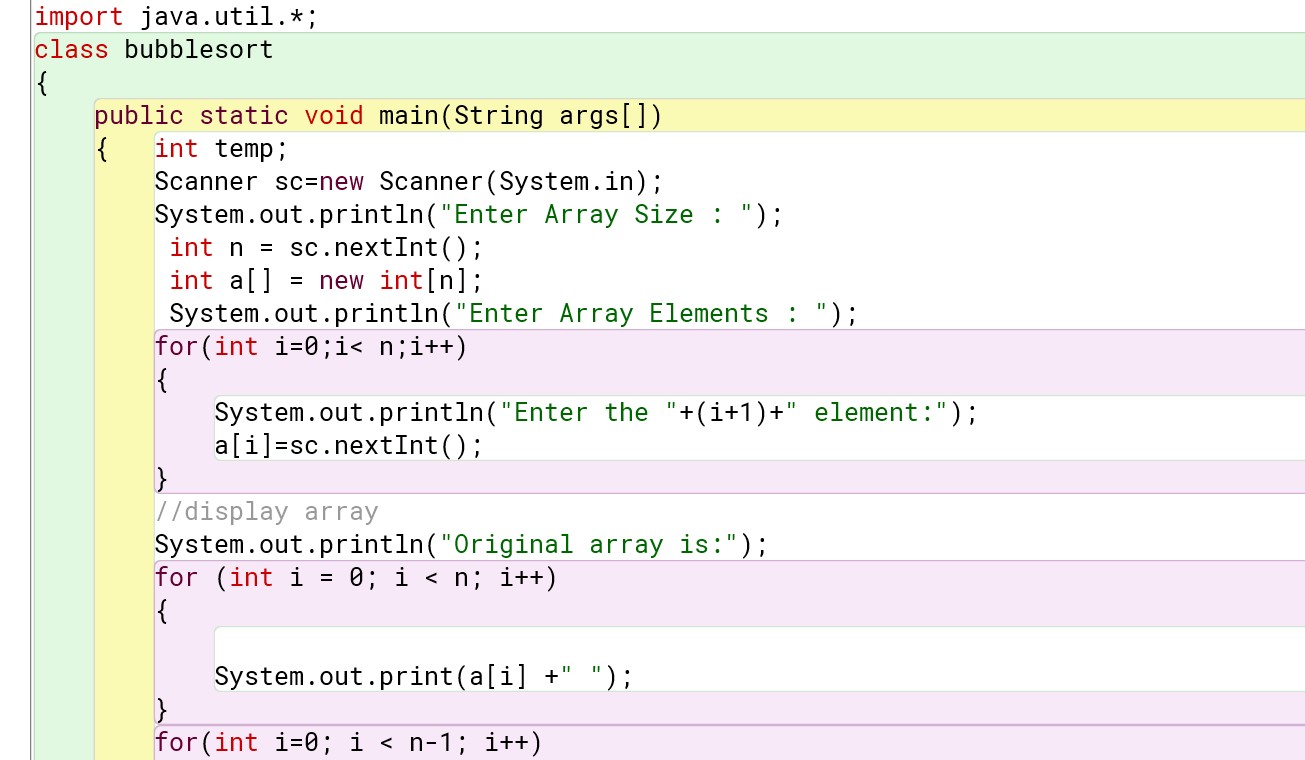

Output :
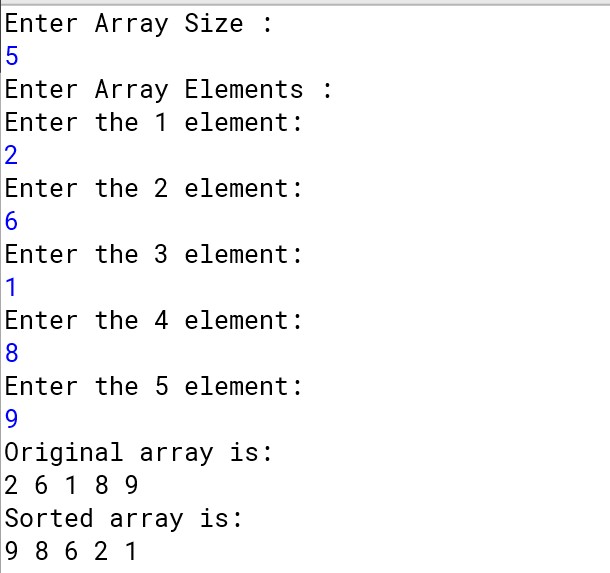
For pre-defined values :
Program :
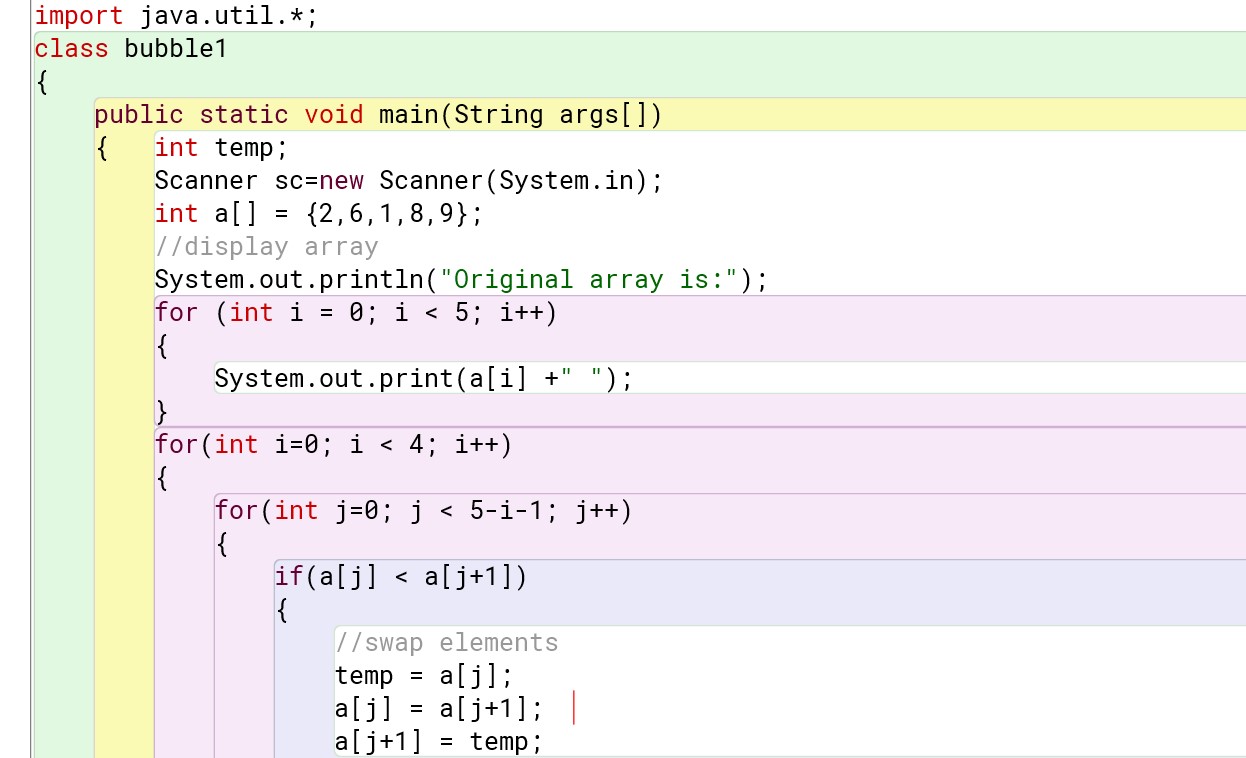

Output :







Output :



Output :

Selection Sort
The selection sort technique is a method in which the smallest element in the array is selected and then swapped with the element that is located in the first position, then the second smallest element in the remaining unsorted array is selected and put in the second position, and so on. Have a look at the implementation explained below.
How Selection Sort works (In ascending order) :
In this technique we do sorting upto (size - 1), if there are 5 elements, it takes (5-1), i.e 4 iterations to completely sort the array.
For 0th index (I Iteration) :
We will store value at zeroth index (i.e. 2) then compare it with all the elements and swap it with the smallest value (i.e. 1 at index 3) as shown below.
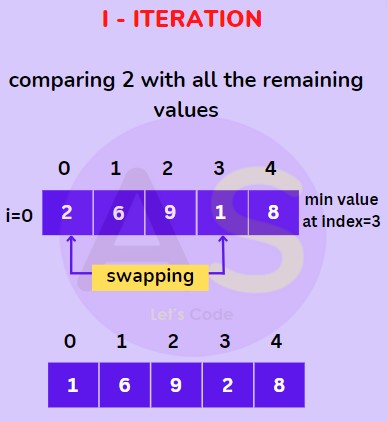
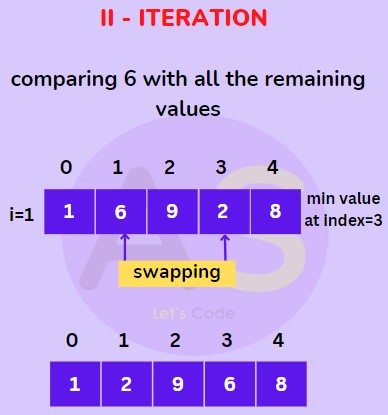
For 1st index (II Iteration) :
We will start with value at first index (i.e. 6) then compare it with all the elements (except the value at zeroth index) and swap it with the smallest value (i.e. 2 at index 3) as shown below.
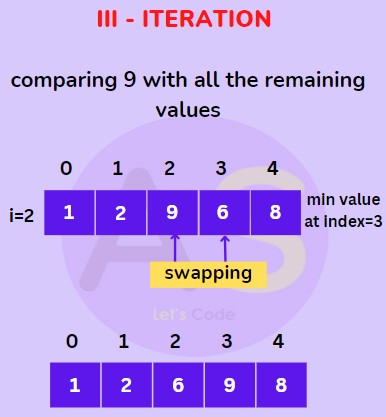
For 2nd index (III Iteration) :
We will start with value at second index (i.e. 9) then compare it with all the elements (except the values at zeroth index & first index) and swap it with the smallest value (i.e. 6 at index 3) as shown below.
For 3rd index (IV Iteration) :
We will start with value at third index which is 9 then compare it with all the elements (except the values at zeroth index , first index & second index ) and swap it with the smallest value (i.e. 8 at index 4) as shown below.
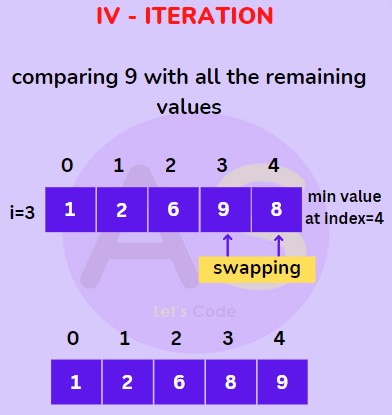
Now, our array is sorted in ascending order.
For user-defined value :
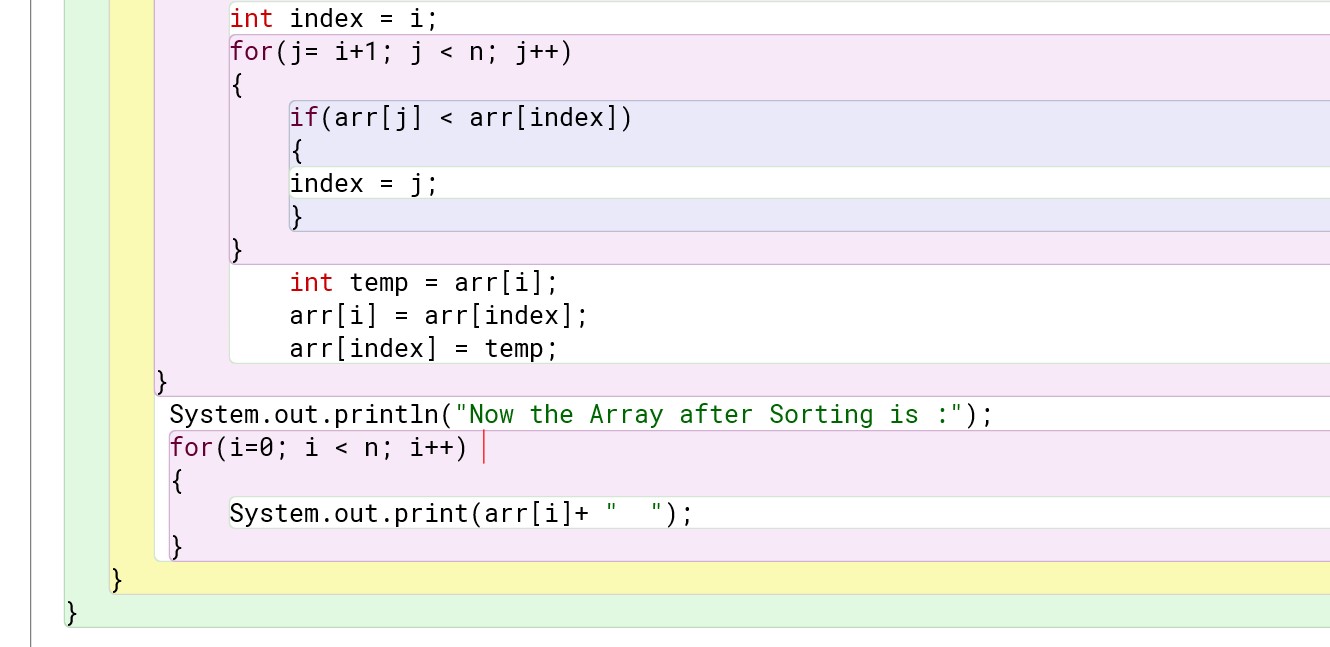
Program :

Output :
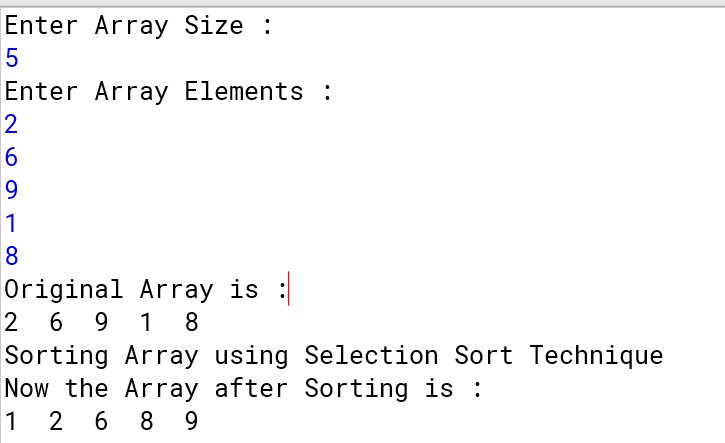
For pre-defined values :
Program :

Output :
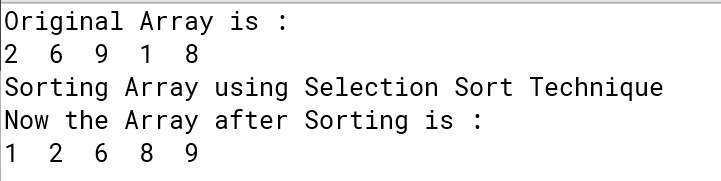






Output :



Output :

Insertion Sort
Insertion sort is a sorting algorithm that places an unsorted element at its suitable place in each iteration.
How Insertion Sort works ( For ascending order) :
Fundamentally, the array gets divided into 2 parts. First part is a sorted and the second one is unsorted.
So in this technique the first element is assumed to be sorted. Take the second element just next to it and store it in temp variable, compare temp with the first element if the first element is greater than the temp then the first element is shifted towards right and temp is placed on its place. Have a look at the implementation explained below.
After every iteration the sorted array gets bigger and unsorted array gets smaller.
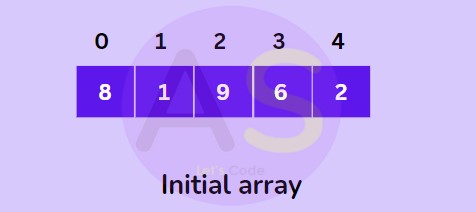
For (I-Iteration) :
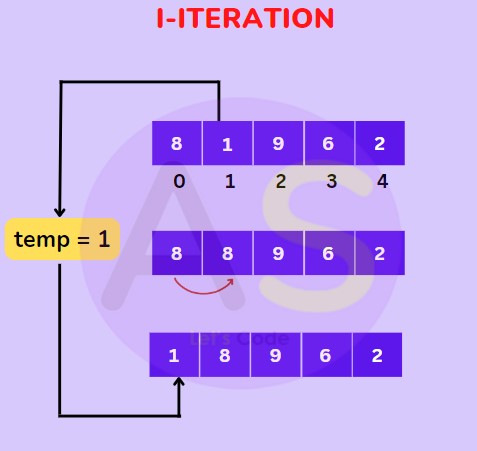
For (II-Iteration) : Now the first two elements are sorted take the 3rd element and compare it with the elements on the left of it. Place it just behind the element smaller than it , if it is not smaller then no shifting will be done the element will be on its place only.
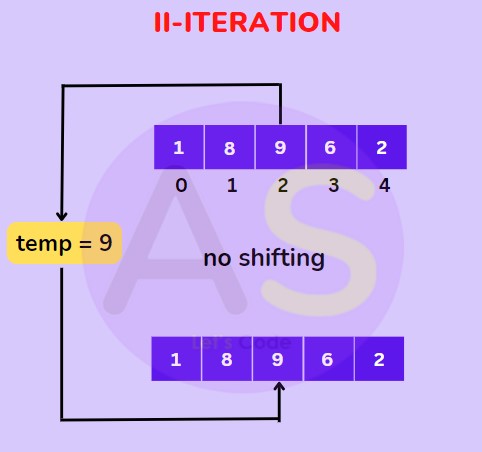
For (III-Iteration) :Now the first three elements are sorted take the 4th element and compare it with the elements on the left of it and place it just behind the element smaller than it.
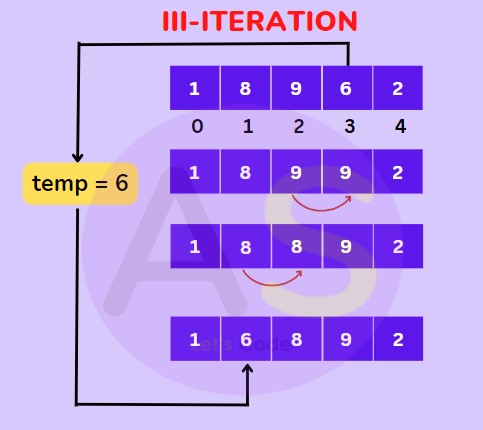
For (IV-Iteration) : Now the first 4 elements are sorted take the 5th element and compare it with the elements on the left of it and place it just behind the element smaller than it.
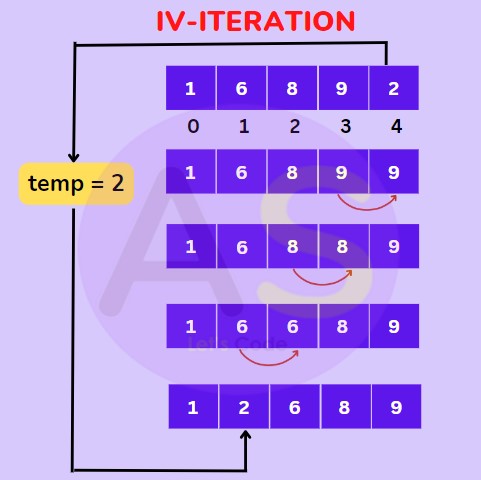
For user-defined values :
Program :
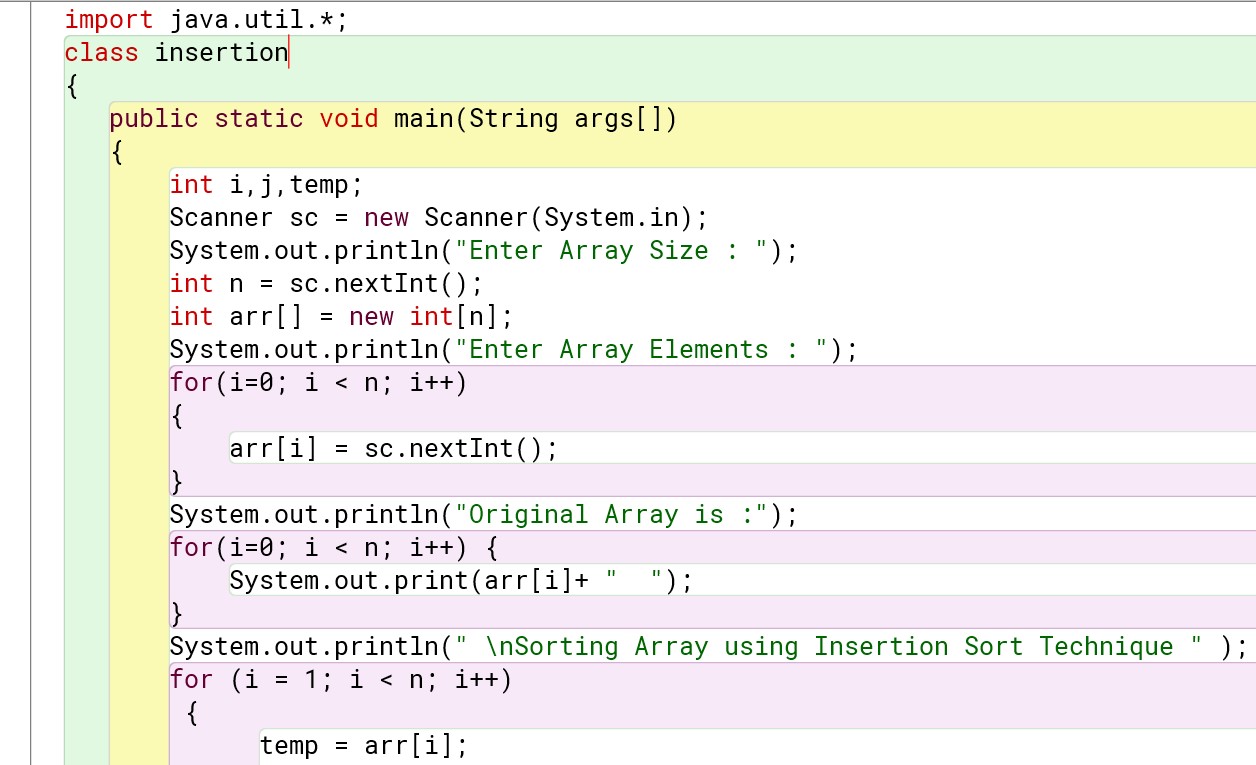

Output :

For pre-defined values :
Program :
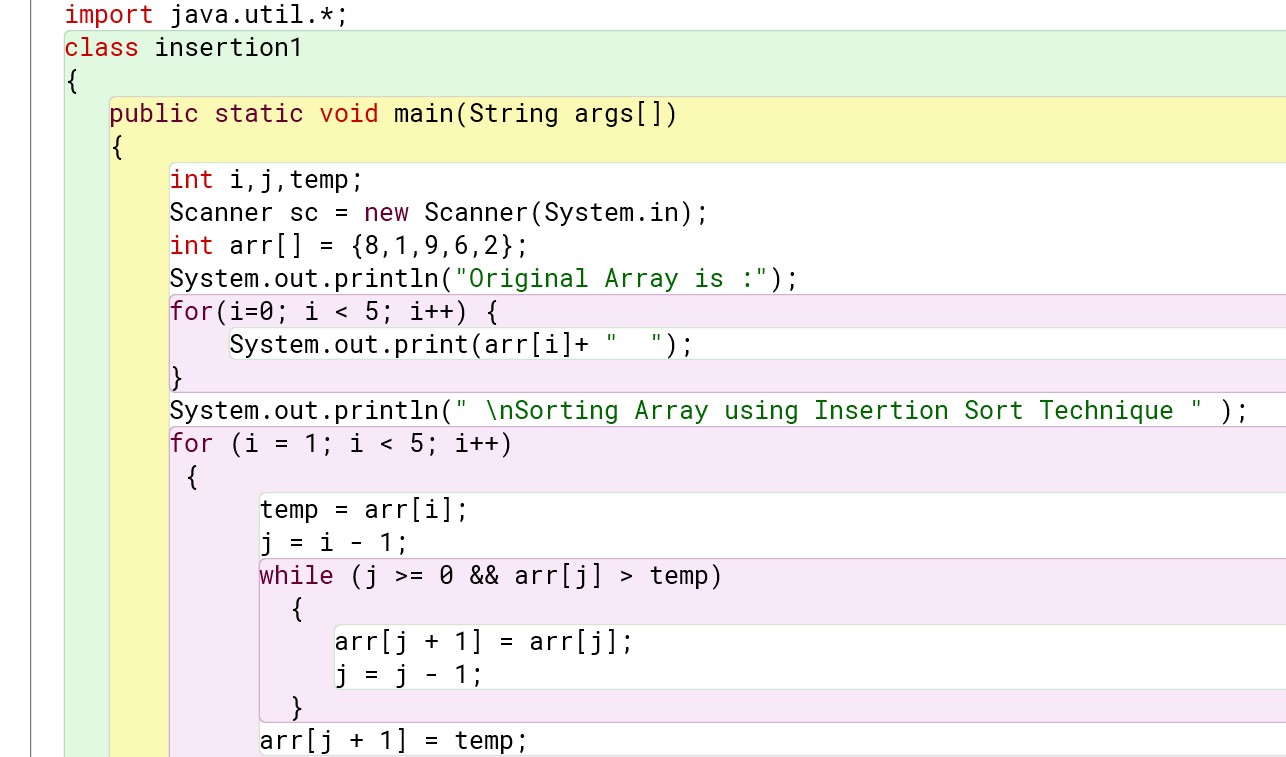
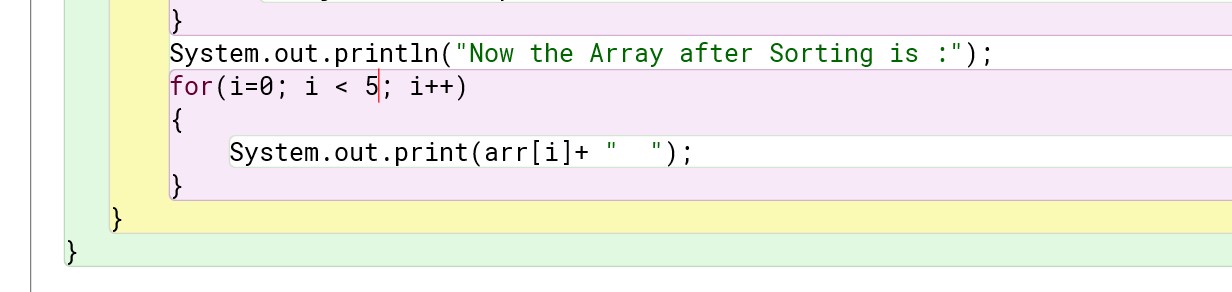
Output :
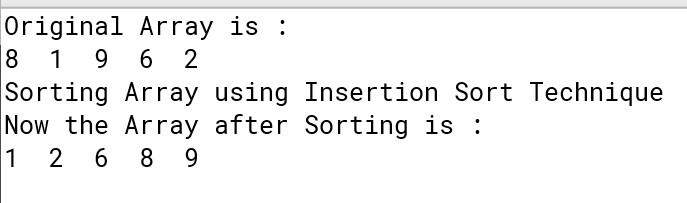







Output :



Output :
