Code is copied!
CLASS 10 ICSE JAVA SPECIMEN PAPER 2022 TERM - II
Maximum Marks:50
Time allowed: One and a half hours
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during the first 10 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the question paper.
The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
This Paper is divided into two Sections.
Attempt all questions from Section A and any four questions from Section B.
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets[] .
SECTION A
(Attempt all questions from this Section.)
Question 1
(i) When primitive data type is converted to its corresponding object of its class, it is called as ___________.
- Boxing
- Explicit type conversion
- Unboxing
- Implicit type conversion
Solution
(a)
Boxing
(ii)
State the value of y after the following is executed:
char x='7';
y= Character.isLetter(x);
- false
- 7
- true
- ‘7’
Solution
(a) (Character.isletter() method checks if a variable is a letter or not so it returns false)
false
(iii)
Give the output of the following string methods:
"MISSISSIPPI".indexOf('S')+ "MISSISSIPPI".lastIndexOf('I')
- 10
- 12
- 20
- 11
Solution
(b) (2+10)
12
(iv) Corresponding wrapper class of int data type is __________.
- integer
- INTEGER
- Int
- Integer
Solution
(d)
Integer
(v) Variable that is declared with in the body of a method is termed as:
- Instance variable
- class variable
- Local variable
- Argument variable
Solution
(c)
Local variable
(vi) Identify the correct array declaration statement:
- int a[10];
- int a[]=new int[10];
- int arr[i]=10;
- int a[10]=new int[];
Solution
(b)
int a[]=new int[10];
(vii) A variable that is bounded to the object itself is called as:
- Instance variable
- class variable
- Local variable
- Argument variable
Solution
(a)
Instance variable
(viii) The access modifier that gives most accessibility is:
- private
- public
- protected
- package
Solution
(b)
public
(ix)
Give the output of the following code:
String A ="26.0", B="74.0";
double C= Double .parseDouble(A);
double D = Double .parseDouble(B);
System.out.println((C+D));
- 26
- 74
- 100.0
- 2674
Solution
(c)(Double.parseDouble() method convert it into double datatype so result will be 100.0)
100.0
(x) Wrapper classes are available in __________ package.
- java.io
- java.util
- java.lang
- java.awt
Solution
(c)
java.lang
SECTION B
(Attempt any four questions.)
Question 2
Define a class to declare an integer array of size n and accept the elements into the array.
Search for an element input by the user using linear search technique, display the element
if it is found, otherwise display the message “NO SUCH ELEMENT.
Solution:
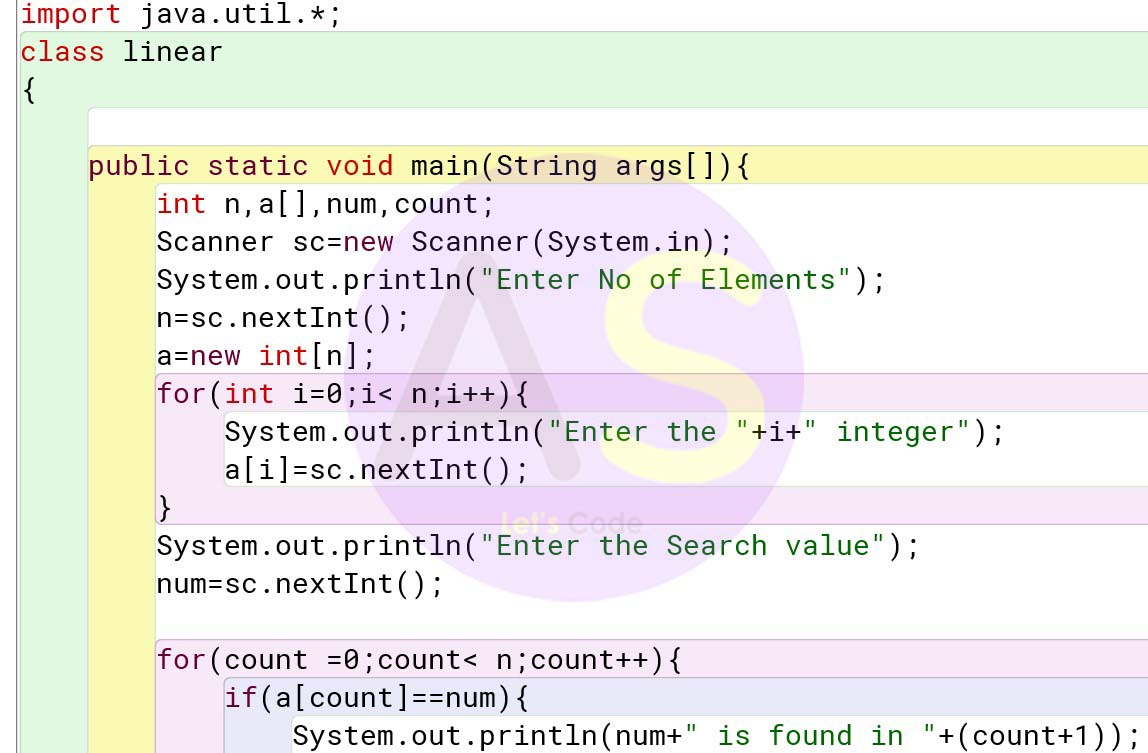

import java.util.*;
class linear
{
public static void main(String args[]){
int n,a[],num,count;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter No of Elements");
n=sc.nextInt();
a=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i< n;i++){
System.out.println("Enter the "+i+" integer");
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Enter the Search value");
num=sc.nextInt();
for(count =0;count< n;count++){
if(a[count]==num){
System.out.println(num+" is found in "+(count+1));
//item is found so to stop the search and to come out of loop we use break statement
break;
}
}
if(count==n){
System.out.println("NO SUCH ELEMENT EXIST");
}
}
}
Question 3
Define a class to declare a character array of size ten, accept the character into the array
and perform the following:
1. Count the number of uppercase letters in the array and print.
2. Count the number of vowels in the array and print.
Solution:
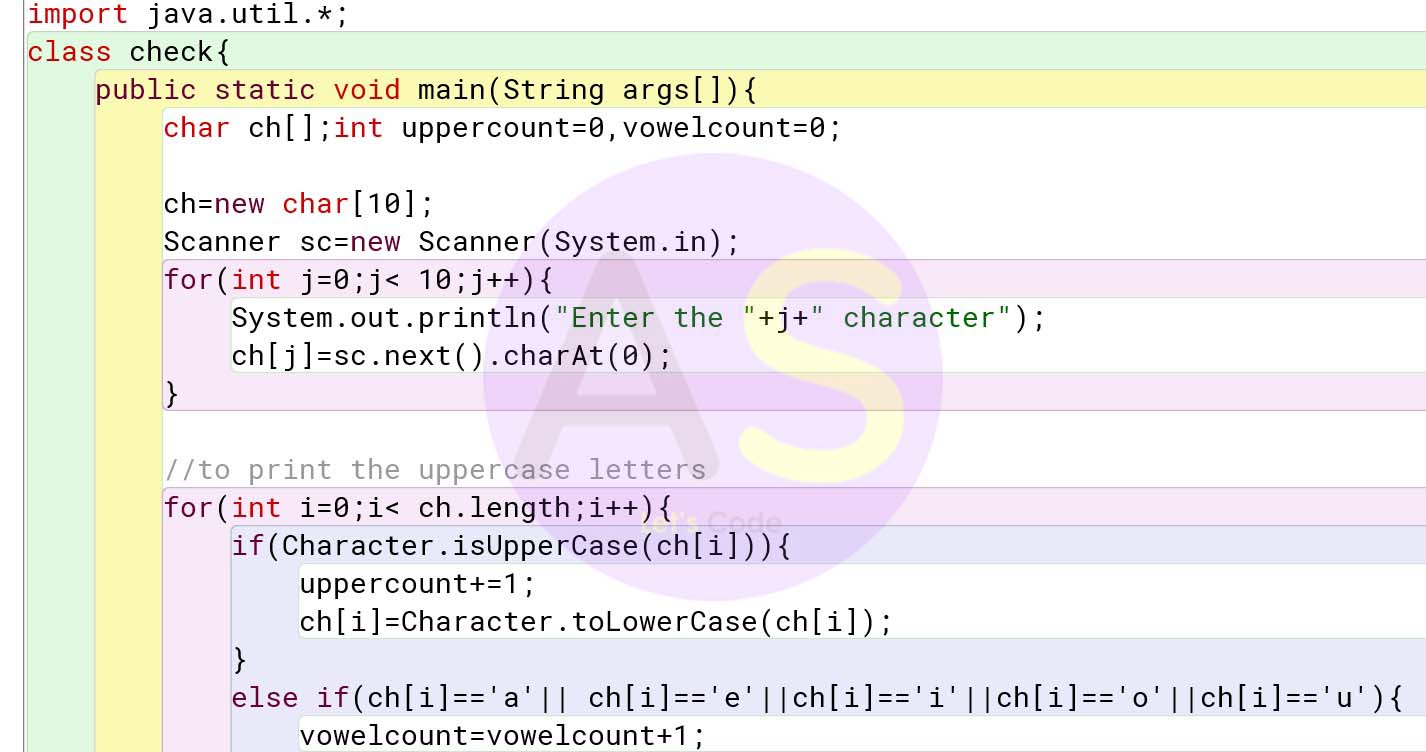

import java.util.*;
class check{
public static void main(String args[]){
char ch[];int uppercount=0,vowelcount=0;
ch=new char[10];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(int j=0;j< 10;j++){
System.out.println("Enter the "+j+" character");
ch[j]=sc.next().charAt(0);
}
//to print the uppercase letters
for(int i=0;i< ch.length;i++){
if(Character.isUpperCase(ch[i])){
uppercount+=1;
ch[i]=Character.toLowerCase(ch[i]);
}
else if(ch[i]=='a'|| ch[i]=='e'||ch[i]=='i'||ch[i]=='o'||ch[i]=='u'){
vowelcount=vowelcount+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Number of UpperCase Letters is="+uppercount);
System.out.println("Number of vowels is="+vowelcount);
}
}
Question 4
Define a class to declare an array of size 20 of double datatype, accept the elements into
the array and perform the following:
1. Calculate and print the sum of all the elements.
2. Calculate and print the highest value of the array.
Solution:
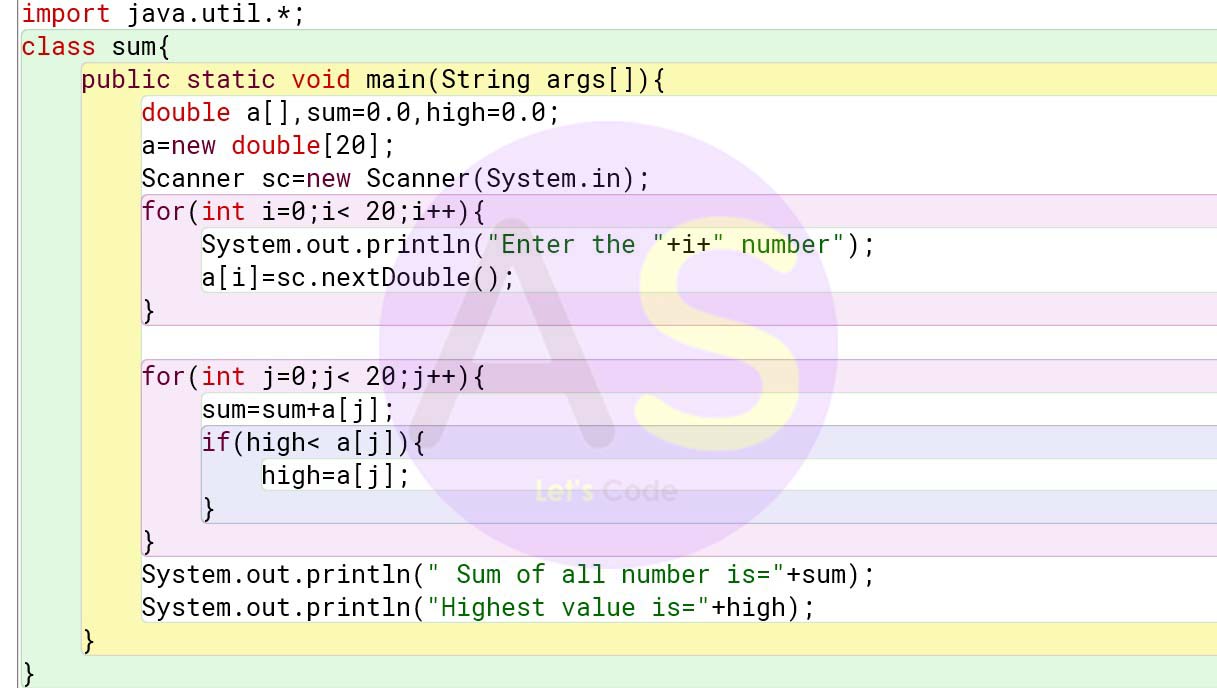
import java.util.*;
class sum{
public static void main(String args[]){
double a[],sum=0.0,high=0.0;
a=new double[20];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i< 20;i++){
System.out.println("Enter the "+i+" number");
a[i]=sc.nextDouble();
}
for(int j=0;j< 20;j++){
sum=sum+a[j];
if(high< a[j]){
high=a[j];
}
}
System.out.println(" Sum of all number is="+sum);
System.out.println("Highest value is="+high);
}
}
Question 5
Define a class to accept two strings, convert them into uppercase, check and display
whether two strings are equal or not, if the two strings are not equal, print the string with
the highest length or print the message both the strings are of equal length.
Solution:
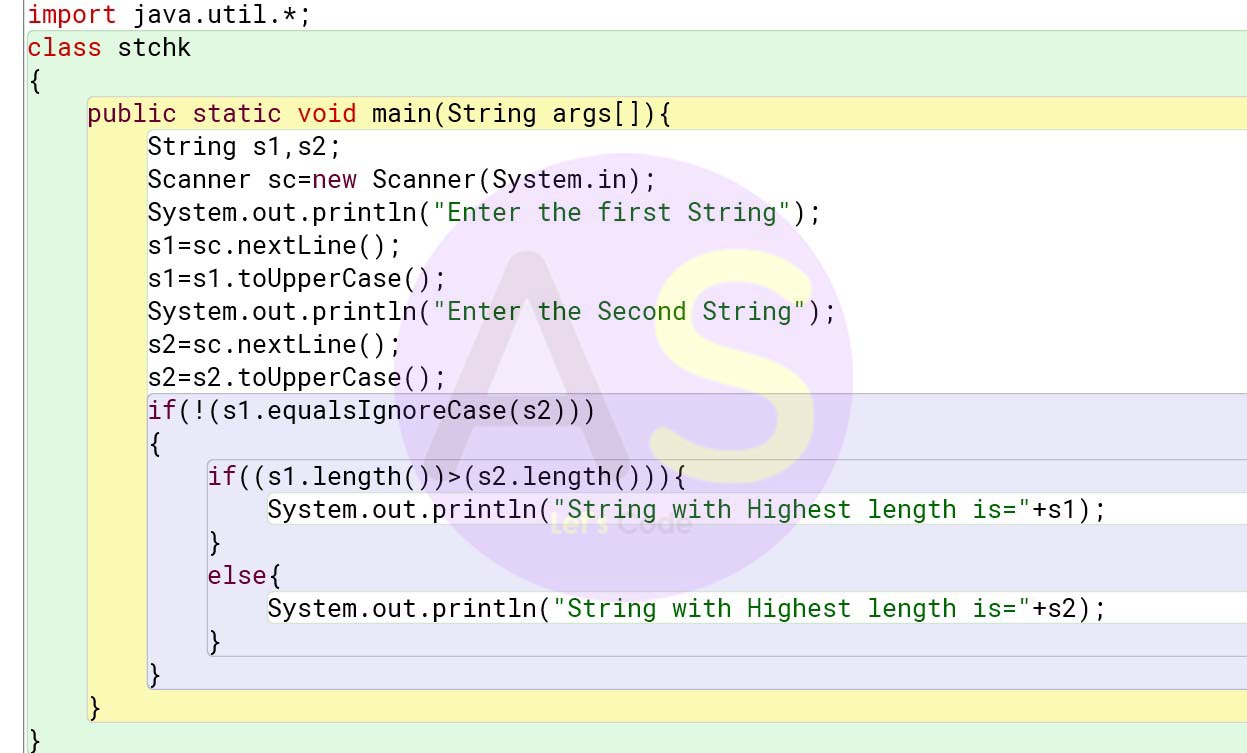
import java.util.*;
class stchk
{
public static void main(String args[]){
String s1,s2;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the first String");
s1=sc.nextLine();
s1=s1.toUpperCase();
System.out.println("Enter the Second String");
s2=sc.nextLine();
s2=s2.toUpperCase();
if(!(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)))
{
if((s1.length())>(s2.length())){
System.out.println("String with Highest length is="+s1);
}
else{
System.out.println("String with Highest length is="+s2);
}
}
}
}
Question 6
Define a class to accept a string, convert it into lowercase and check whether the string is
a palindrome or not.
A palindrome is a word which reads the same backward as forward.
Example:
madam, racecar etc.
Solution:
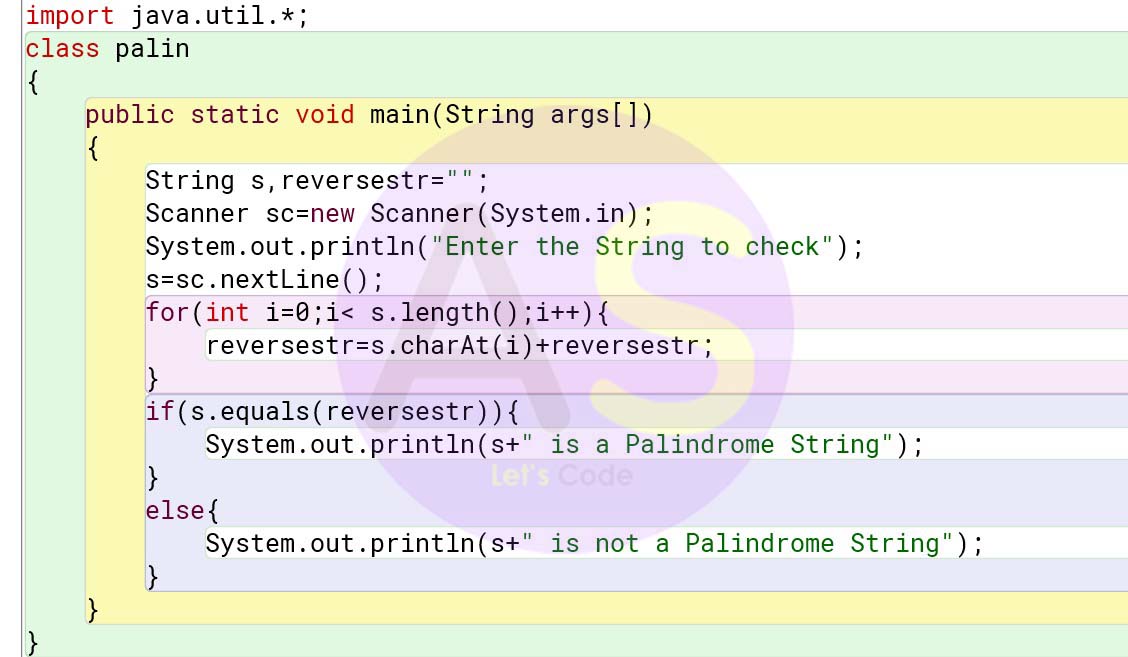
import java.util.*;
class palin
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s,reversestr="";
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the String to check");
s=sc.nextLine();
for(int i=0;i< s.length();i++){
reversestr=s.charAt(i)+reversestr;
}
if(s.equals(reversestr)){
System.out.println(s+" is a Palindrome String");
}
else{
System.out.println(s+" is not a Palindrome String");
}
}
}
Question 7
Define a class to accept and store 10 strings into the array and print the strings with even
number of characters.
Solution:
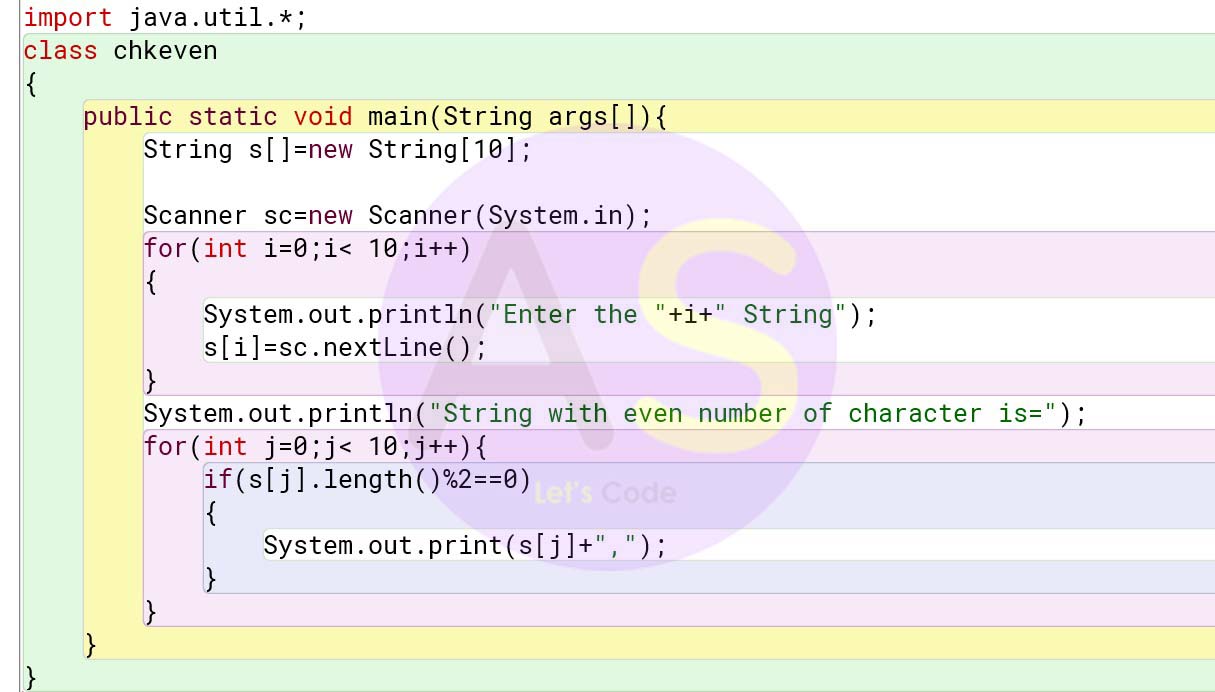
import java.util.*;
class chkeven
{
public static void main(String args[]){
String s[]=new String[10];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i< 10;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the "+i+" String");
s[i]=sc.nextLine();
}
System.out.println("String with even number of character is=");
for(int j=0;j< 10;j++){
if(s[j].length()%2==0)
{
System.out.print(s[j]+",");
}
}
}
}