Class 10 ICSE - Java
Class 10th Java aims to empower students by enabling them to build their own applications introducing some effective tools to enable them to enhance their knowledge, broaden horizons, foster creativity, improve the quality of work and increase efficiency.
It also develops logical and analytical thinking so that they can easily solve interactive programs. Students learn fundamental concepts of computing using object oriented approach in one computer language with a clear idea of ethical issues involved in the field of computing
Class 10th java topics includes revision of class 9th, constructors, user-defined methods, objects and classes, library classes , etc.
Arrays & its uses
Introduction to Array
- An array is a collection of similar types of data having contiguous memory allocation.
- The indexing of the array starts from 0., i.e 1st element will be stored at the 0th index, 2nd
element at 1st index, 3rd at 2nd index, and so on.
- The size of the array can not be increased at run time therefore we can store only a fixed size of
elements in array.
-
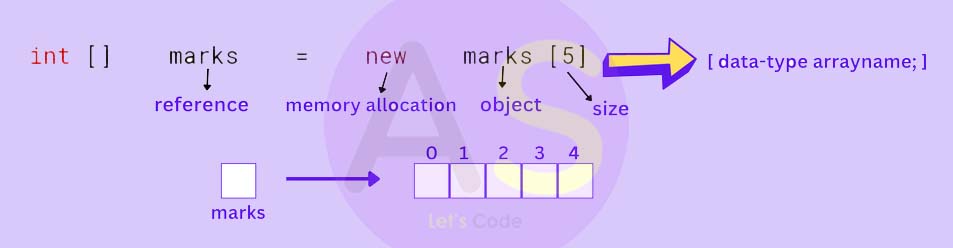
Example of storing marks of 5 students :
Accessing array elements :

So , this is how array works:
int [] marks; ;⇛ Declaration!
marks = new int[5]; ⇛ Memory allocation!
int [] marks = new int[5]; ⇛ Declaration + Memory
allocation!
int [] marks = {100, 70, 80, 71, 98} ⇛ Declare +
Initialize!
Note : Array indices start from 0 and go till (n-1) where n is the size of the
array.


marks = new int[5]; ⇛ Memory allocation!
int [] marks = new int[5]; ⇛ Declaration + Memory allocation!
int [] marks = {100, 70, 80, 71, 98} ⇛ Declare + Initialize!
Note : Array indices start from 0 and go till (n-1) where n is the size of the
array.
Creating & Displaying Array
⇛ Creation of Array :
There are three main ways to create an array :
(i) Declaration and memory allocation
// int[] marks = new int[5];
(ii) Declaration and then memory allocation
int [] marks;
marks = new int[5];
Initialization
marks[0] = 100;
marks[1] = 60;
marks[2] = 70;
marks[3] = 90;
marks[4] = 86;
(iii) Declaration, memory allocation and initialization together
int[] marks = {98, 45, 79, 99, 80};
⇛ Displaying array :
An array can be displayed using a for loop:

marks = new int[5];
Initialization
marks[0] = 100;
marks[1] = 60;
marks[2] = 70;
marks[3] = 90;
marks[4] = 86;

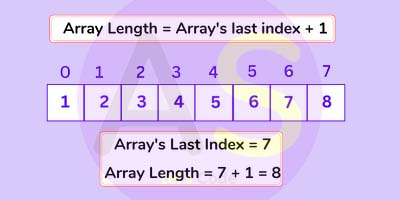
Array Length
The array length is the number of elements that an array can hold. There is no predefined method to obtain
the length of an array. We can find the array length by using the array "length" property. The "length"
property determines the length of an array.
The length property can be invoked by using the dot (.) operator followed by the array name.
For Example :
int[] arr=new int[5];
int Length = arr.length;
In the above example, arr is an array of type int that can hold 5 elements. The Length is a variable that
stores the length of an array. To find the length of the array, we have used array name (arr) followed by
the dot operator (.) and length property, respectively. It determines the size of the array.
int Length = arr.length;
