Code is copied!
Define a class to overload the method print as follows:
void print () — to print the format
1
2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 10
boolean print (int n) — to check whether the number is a Dudeney number ,a number is dudeney if the cube of the sum of the digits is equal to the number itself.
Eg : 512 = (5+1+2)3 =(8)3 = 512
void print (int a, char ch) — if ch = s or S print the square of the number else if ch =c or C print the cube of the number.
Solution:
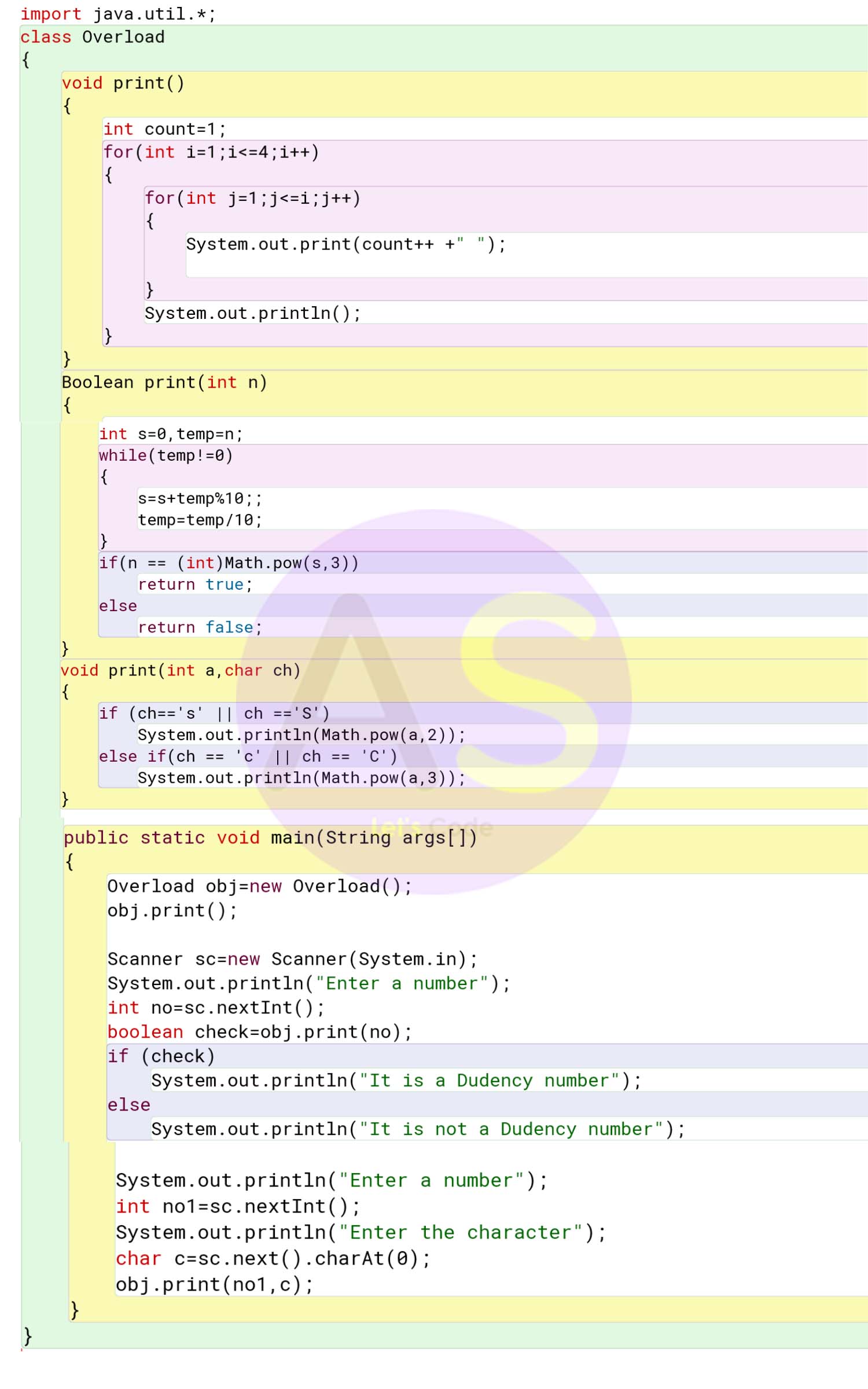
import java.util.*;
class Overload
{
void print()
{
int count=1;
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
System.out.print(count++ +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Boolean print(int n)
{
int s=0,temp=n;
while(temp!=0)
{
s=s+temp%10;;
temp=temp/10;
}
if(n == (int)Math.pow(s,3))
return true;
else
return false;
}
void print(int a,char ch)
{
if (ch=='s' || ch =='S')
System.out.println(Math.pow(a,2));
else if(ch == 'c' || ch == 'C')
System.out.println(Math.pow(a,3));
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Overload obj=new Overload();
obj.print();
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number");
int no=sc.nextInt();
boolean check=obj.print(no);
if (check)
System.out.println("It is a Dudency number");
else
System.out.println("It is not a Dudency number");
System.out.println("Enter a number");
int no1=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the character");
char c=sc.next().charAt(0);
obj.print(no1,c);
}
}