Code is copied!

Define a class Trr with the following data members
int arr[3][3] and following functions
void input() - To input a 3x3 matrix
Transpose() To return transfers of matrix arr[][]
Trrproduct(Trr M) - To return the product of current and the transposed matrix M
void display() - To display the matrix it transpose and the product in the following format:
1 3 1 1 2 9 11 21 21
2 4 7 x 3 4 2 = 21 69 68
9 2 6 1 7 6 21 68 121



import java.util.*;
class Trr
{
int arr[][]=new int[3][3];
void input()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter 3X3 Matrix");
for(int i=0;i< 3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j< 3;j++)
{
arr[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
}
}
Trr transpose()
{
Trr m=new Trr();
for(int i=0;i< 3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j< 3;j++)
{
m.arr[i][j]=arr[j][i];
}
}
return m;
}
Trr product(Trr m)
{
Trr x=new Trr();
int s=0;
for(int i=0;i< 3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j< 3;j++)
{
s=0;
for(int k=0;k< 3;k++)
{
s=s+(arr[i][k]*m.arr[k][j]);
}
x.arr[i][j]=s;
}
}
return x;
}
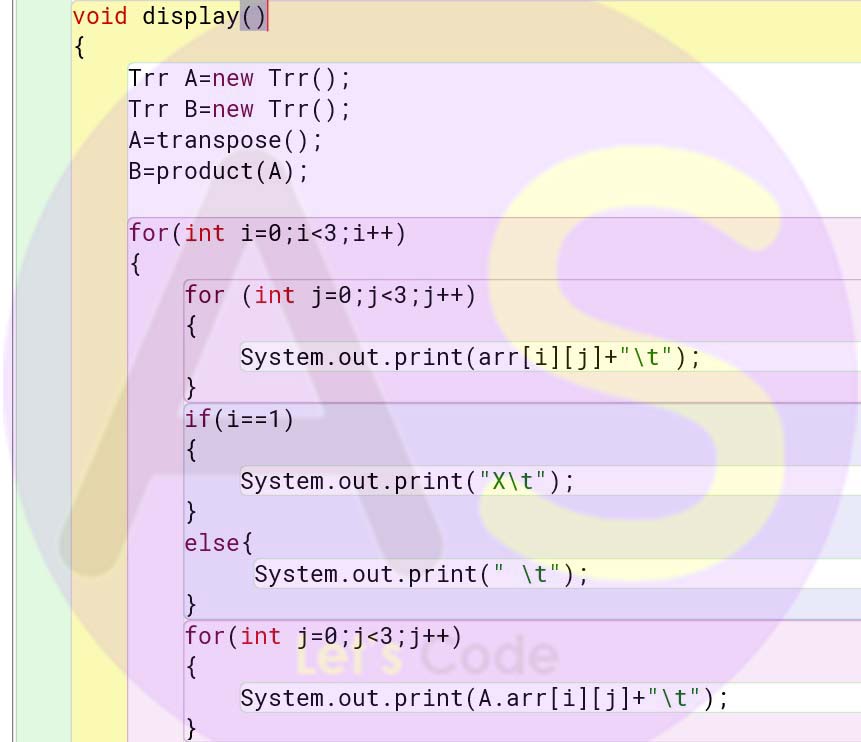
void display()
{
Trr A=new Trr();
Trr B=new Trr();
A=transpose();
B=product(A);
for(int i=0;i< 3;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j< 3;j++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+"\t");
}
if(i==1)
{
System.out.print("X\t");
}
else{
System.out.print(" \t");
}
for(int j=0;j< 3;j++)
{
System.out.print(A.arr[i][j]+"\t");
}
if(i==1)
{
System.out.print("=\t");
}
else{
System.out.print(" \t");
}
for(int j=0;j< 3;j++)
{
System.out.print(B.arr[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Trr obj=new Trr();
obj.input();
obj.display();
}
}