Code is copied!

A set is a collection in which there is no duplication of elements a multi set is a collection in which elements can be duplicate for example
S = {1,2,3,4} is a set with integer elements.
while
ms = {1,2,3,1,3} is a multiset with integers elements.
Following are some member function of class multiset which defines multi set with integer elements
Class Name Set
Data members / instance variables
Intarr[] integers array of size n
Int n [size]
Member Functions / methods:
Set() - Constructor to assign zero to n
Set(int nn) - Constructor to assign n = nn
intisset(set s) - returns 1(one) if the multiset object is a set and 0(zero) otherwise.
Set intersection(Set s1, Set s2) returns intersection elements of s1,s2 assume that s1 and s2 are sets.
Void displaylist() - to display the intersection elements if both are set. Else display "multiset".
Also write main().






import java.util.*;
class Set
{
int arr[];
int n;
Set()
{
n = 0;
}
Set(int nn)
{
n = nn;
}
void readlist()
{
arr = new int[n];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter element " + (i));
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
int isset()
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int flag = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(j = (i + 1); j < n; j ++)
{
if(arr[i] == arr[j])
{
flag = 1;
}
}
}
if(flag == 1)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
Set intersection(Set s1, Set s2)
{
int i = 0;
int a[] = new int[s1.n];
int j = 0;
int c = 0;
for(i = 0; i < s1.n; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < s2.n; j++)
{
if(s1.arr[i] == s2.arr[j])
{
a[c] = s1.arr[i];
c++;
break;
}
}
}
Set s3 = new Set();
s3.n = c;
s3.arr = new int[s3.n];
for(i = 0; i < s3.n; i++)
{
s3.arr[i] = a[i];
}
return s3;
}
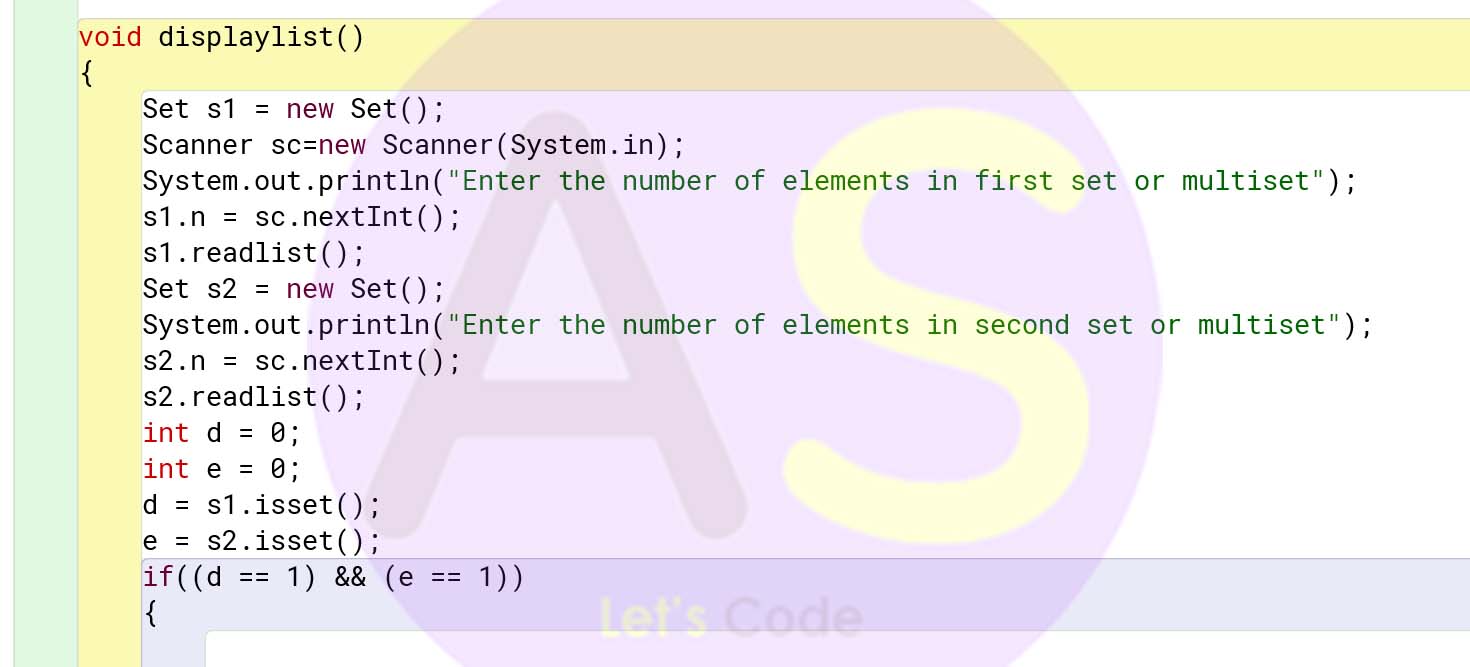
void displaylist()
{
Set s1 = new Set();
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of elements in first set or multiset");
s1.n = sc.nextInt();
s1.readlist();
Set s2 = new Set();
System.out.println("Enter the number of elements in second set or multiset");
s2.n = sc.nextInt();
s2.readlist();
int d = 0;
int e = 0;
d = s1.isset();
e = s2.isset();
if((d == 1) && (e == 1))
{
Set s3 = new Set();
s3 = intersection(s1, s2);
System.out.println("The intersection elements are");
int i = 0;
if(s3.n == 0)
System.out.println("No intersection element");
for(i = 0; i < s3.n; i++)
{
System.out.println(s3.arr[i]);
}
}
else
System.out.println("Multiset");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Set A = new Set();
A.displaylist();
}
}