Code is copied!
A class Encode has been defined to replace only the vowels in a word by the next
corresponding vowel and form a new word.
i.e. A → E, E → I, I → O, O → U, U → A and
a → e, e → i, i → o, o → u, and u → a
Example: Input: Institution
Output: Onstotatoun
Some of the members of the class are given below:
Class name : Encode
Data members/instance variables:
word : to store a word
length : integer to store the length of the word
new_word : to store the encoded word
Methods / Member functions:
Encode( ) : default constructor to initialize data members
with legal initial values
void acceptWord( ) : to accept a word
void nextVowel( ) : to replace only the vowels from the word stored
in ‘word’ by the next corresponding vowel and
to assign it to ‘newword’, with the remaining
alphabets unchanged
void display( ) : to display the original word along with the
encrypted word
Specify the class Encode giving details of the constructor( ), void acceptWord( ),
void nextVowel( ) and void display( ). Define a main ( ) function to create an object and
call the functions accordingly to enable the task
Solution:
 ,
, ,
,
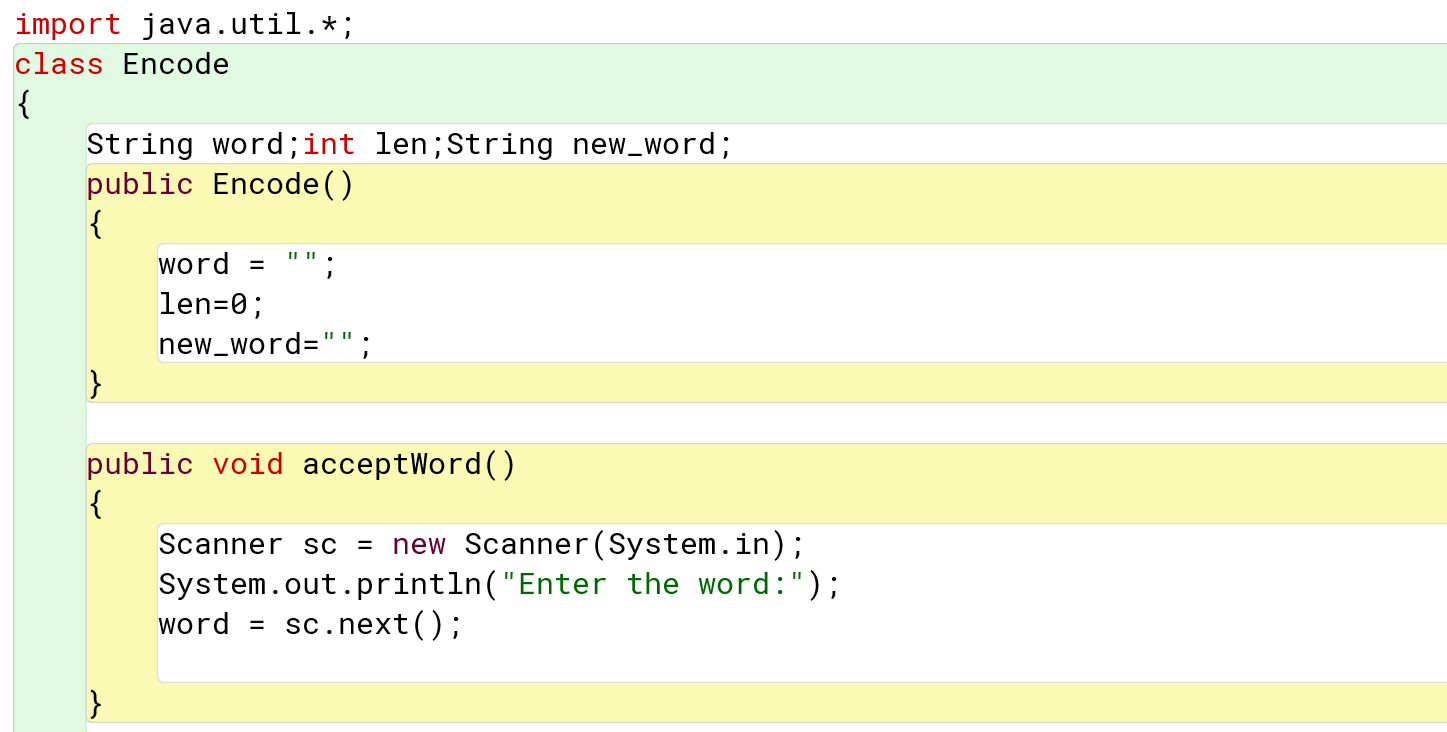
import java.util.*;
class Encode
{
String word;int len;String new_word;
public Encode()
{
word = "";
len=0;
new_word="";
}
public void acceptWord()
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the word:");
word = sc.next();
}
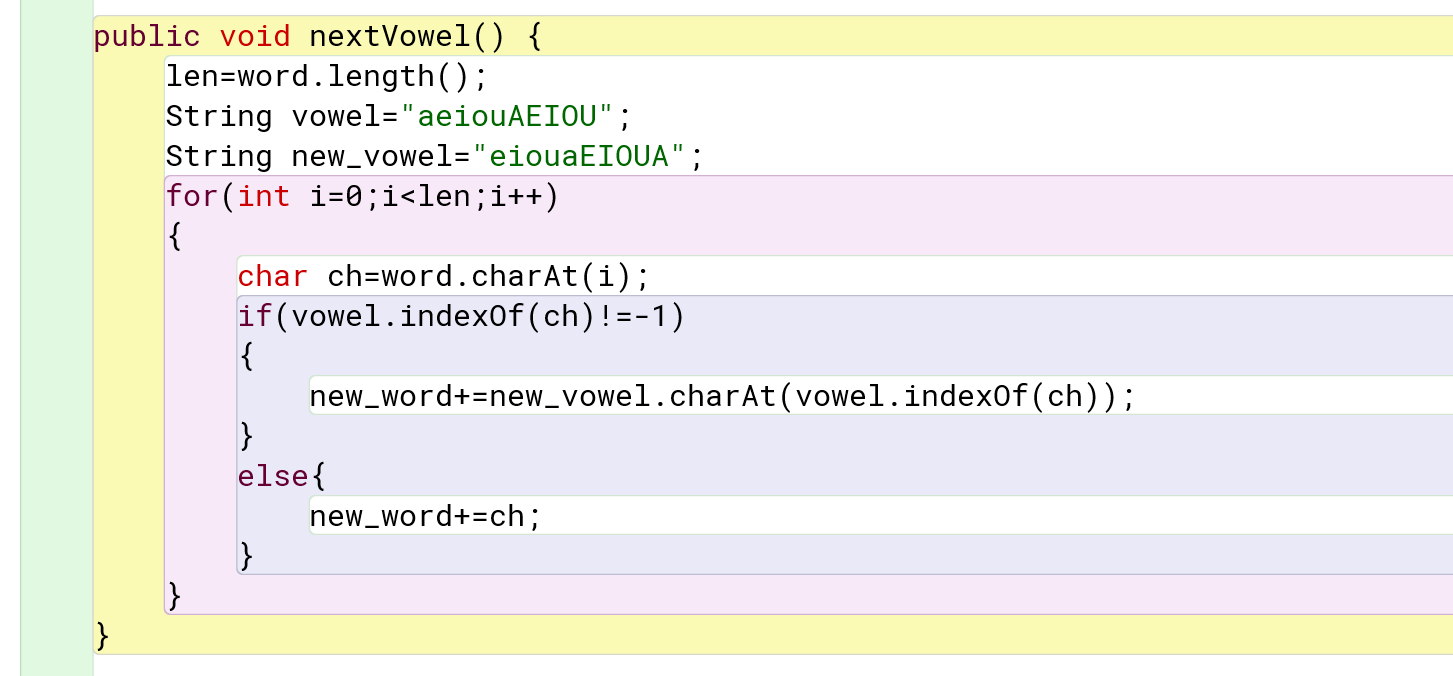
public void nextVowel() {
len=word.length();
String vowel="aeiouAEIOU";
String new_vowel="eiouaEIOUA";
for(int i=0;i< len;i++)
{
char ch=word.charAt(i);
if(vowel.indexOf(ch)!=-1)
{
new_word+=new_vowel.charAt(vowel.indexOf(ch));
}
else{
new_word+=ch;
}
}
}
public void display()
{
System.out.println("Original String="+word);
System.out.println("Encoded String="+new_word);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Encode obj = new Encode();
obj.acceptWord();
obj.nextVowel();
obj.display();
}
}